TS/MP 2.5 System Management Manual
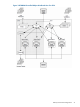
Figure 8 System Management Interfaces
PATHCOM is an interactive, text-based interface; for example, an operator using PATHCOM can
easily start and stop objects or obtain status information about objects. A management programming
interface is command-driven and more toward logical processes. A management programming
interface can simplify the automation of tasks associated with starting, maintaining, and stopping
an environment or maintaining a state.
Whether you use the PATHCOM interactive interface or the management programming interface
to manage your PATHMON environment might depend on the complexity and frequency of your
system management tasks. The more complex or repetitive your system management tasks, the
more advantageous it is to use a management programming interface.
Your choice might also depend on the availability of resources to develop a management
application, which is a sophisticated programming assignment, or on the availability of other
products, such as NonStop NET/MASTER. (NonStop NET/MASTER belongs to the set of HP
management products known collectively as Distributed Systems Management (DSM), which is
described in “Distributed Systems Management” (page 31).)
NOTE: PDMCOM does not support SPI commands.
PATHCOM Interactive Interface
PATHCOM provides commands for defining and managing a PATHMON environment. PATHCOM
also provides online help and error messages.
PATHCOM functions, usage, and command syntax are given in “Overview of PATHCOM” (page 126)
through “SERVER Commands” (page 177) of this manual. A summary of PATHCOM command
syntax is displayed in “Syntax Summary” (page 309).
Using PATHCOM, which consists of sets of object-related commands, you can interactively define
and manage all PATHMON-controlled objects. PATHCOM runs some of these object-related
commands; other commands are processed by the PATHMON process and might involve one or
more TCP or ACS subsystem processes in the execution. For example:
• You define PATHMON-controlled object configurations, start and stop objects, and obtain
status information about objects by entering commands that PATHCOM passes directly to the
PATHMON process.
• You request server-class performance statistics by issuing a STATS SERVER command.
PATHCOM passes the request directly to the PATHMON process, which passes the request
to the link managers, such as the TCPs and ACS subsystem processes. The link managers run
30 Introduction to NonStop TS/MP System Management