TS/MP System Management Manual (H06.05+, J06.03+)
Introduction to NonStop TS/MP System
Management
HP NonStop TS/MP System Management Manual—541819-007
1-15
Unsupported or Special-Function I/O Devices
The application interface to SNAX/HLS requires little detailed knowledge of SNAX or
SNA. For more information about the SNAX/HLS product, see the SNAX/HLS
Configuration and Control Manual.
Unsupported or Special-Function I/O Devices
Requests from unsupported or special-function I/O devices can be handled by the HP
Extended General Device Support (GDSX) product. GDSX is designed to help you
develop a front-end process that translates requests into a format supported by
LINKMON process, ACS subsystem processes, or (under Pathway/iTS) a TCP.
GDSX is a complex product. Before choosing to use GDSX, determine whether the
LINKMON process or the ACS subsystem processes can manage the requests alone.
If your environment includes Pathway/iTS, investigate whether the PATHMON process
and TCP can handle your application requirements. If the specified data
communications protocols are not supported by existing Pathsend requesters or (under
Pathway/iTS) a TCP, you might decide to use a GDSX process as a front end to the
application.
Using the GDSX product, you can implement message switching, develop and modify
data communications protocols, and perform data-stream conversions, all of which
facilitate access to server processes. For more information about the GDSX product,
see the Extended General Device Support (GDSX) Manual.
Pathsend Processes
Pathsend processes (also called Pathsend requesters) are user applications that
access server classes using Pathsend procedure calls. These procedure calls are part
of the Guardian procedure library. RSC and POET workstation clients are examples
of applications that communicate with server processes indirectly by means of
Pathsend requesters created by RSC on behalf of the clients. LINKMON processes or
ACS subsystem processes manage communicatons between Pathsend processes and
server classes. System management issues related to Pathsend are described in
Section 6, Managing the Pathsend Environment of this manual. (For information about
how to write Pathsend programs, see the TS/MP Pathsend and Server Programming
Manual).
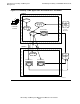
Figure 1-6 shows a PATHMON environment with Pathsend requesters. Link
management functions for Pathsend requesters are provided by the LINKMON
processes $ZL01 and $ZL02. LINKMON process or ACS subsystem processes
service requests only from Pathsend processes executing in its processor. $PMB is the
PATHMON process controlling the pathway environment.