COBOL Manual for TNS/E Programs (H06.08+, J06.03+)
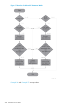
Conditional Form
condition
is any conditional expression (see Conditional Expressions (page 265)).
statement-1
is an imperative or conditional statement to be executed if the value of condition is TRUE.
It can contain other IF statements.
NEXT SENTENCE
specifies that control be passed directly to the end of the sentence containing the IF statement.
It is not recommended (see “Conditional Form” (page 338)).
ELSE
ends statement-1.
statement-2
is an imperative or conditional statement to be executed if the value of condition is FALSE.
It can contain other IF statements.
Usage Considerations:
• CONTINUE and END-IF Are Recommended Over NEXT SENTENCE
NEXT SENTENCE transfers control to the next period (.) while CONTINUE transfers control
to END-IF. Either or both statement-1 and statement-2 can be CONTINUE statements.
• IF Sentences
A conditional IF statement followed by a period separator is called an “IF sentence.” An IF
sentence can contain IF statements (of either form) only if such IF statements do not end with
period separators.
• Nested Conditional IF Statements
Conditional IF statements can be “nested” (included) within other conditional IF statements.
When conditional IF statements are nested, each optional ELSE phrase is considered to be
the next phrase of the nearest preceding unterminated conditional IF statement with which
that phrase is permitted to be associated according to the syntax of the conditional IF statement,
but with which no such phrase has already been associated. An unterminated statement is
338 Procedure Division Verbs