Expand Configuration and Management Manual (H06.21+, J06.10+)
Planning for ServerNet Clusters
Expand Configuration and Management Manual — 529522-013
4 - 5
Examples of ServerNet Clusters Coexisting With
ATM or IP
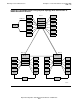
ServerNet Clusters Connected By a Single ATM or IP Line
(Not Recommended)
This topology is not recommended as a solution for enabling communication between
two ServerNet clusters because of higher processor use, traffic bottlenecks, and a lack
of overall network fault tolerance.
Processor use is higher whenever traffic flows between the two ServerNet clusters
because of a technology change between \HHH and \DDD which causes the Exp
and
line handlers to be used at every node on the route (including the source and
destination nodes). For example, when \GGG requests information from \CCC, six
Expand line handlers are invoked: one in \GGG, two in \DDD, two in \HHH, and one in
\CCC.
Line-handler passthrough traffic uses at least twice as much processor time as does
direct traffic. Traffic bottlenecks can occur at \HHH and \DDD when numerous requests
for information are made by systems located on separate ServerNet clusters. Overall
network fault tolerance is not preserved. If \HHH or \DDD becomes unavailable, the
two ServerNet clusters are isolated from each other.
Figure 4-1. ServerNet Clusters Connected by ATM or IP Lines
Note. The Integrity NonStop NS1000 server does not support ServerNet clusters.
\BBB #2
Cluster
Switch
\AAA #1
\GGG #9\CCC #3
Cluster
Switch
\DDD #7
\EEE #5\FFF #4
\HHH #6
\JJJ #8
5-Node ServerNet Cluster 4-Node ServerNet Cluster
ATM or IP
ATM
or IP
ATM or IP
ATM or IP
VST062