Introduction to Networking for NonStop NS-Series Servers (H06.03+, J06.03+)
Networking on Integrity NonStop Servers
Introduction to Networking for HP Integrity NonStop NS-Series Servers—529874-003
1-10
Integrity NonStop Server Networking Compared to
Other Platforms
that all the web server processes are accessing up-to-date information. In a NonStop
server environment, those n hosts can be consolidated onto a single system and have
access to a shared database on that same system.
Returning to the Nonstop TCP/IPv6 subsystem architectural feature of allowing
multiple server processes to bind to a shared port and IP address, the web server
process can run 16 copies of itself and access a shared database while presenting a
single image to the network.
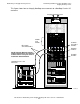
Figure 1-4 shows round-robin filtering on a single IP address. Incoming connection
requests are distributed among 16 instances of the server process in 16 different
processors.
Scaling Your Application on the NonStop System
Several listener models are discussed in the TCP/IPv6 Configuration and Management
Manual, each with unique configuration requirements depending on how that particular
listener model works. By configuring your NonStop TCP/IPv6 subsystem to use round-
robin filtering, you can cause incoming connection requests to be distributed among
different application instances running in different processors.
Round-robin filtering configuration for an application requires that you configure the
NonStop TCP/IPv6 environment with round-robin filtering and that you define the
Figure 1-4. Round -Robin Filtering in the NonStop TCP/IPv6 Environment
Note. To enable NonStop TCP/IPv6 round-robin filtering only for certain applications, you can
limit the ports upon which round-robin filtering is enabled by adding a DEFINE. See the
TCP/IPv6 Configuration and Management Manual for an explanation of this DEFINE.
vst030.vsd
Processors 0 - 2 Processors 3 - 5 Processors 6 - 8 Processors 9 - 11 Processors 12 - 15
G4SA
webserverwebserverwebserverwebserverwebserver