NonStop Server for Java 6.0 Programmer's Reference
Floating-Point Support
By default, NonStop Server for Java 3.1.x and earlier versions converted any floating-point value
that crossed the Java Native Interface (JNI) boundary to a TNS float. This default could be overridden
by supplying a line in the file TandemVMClassFP.properties. If a particular class needed
IEEE floating-point values passed to its JNI code instead of TNS float values; users added a property
(with the name of the class being the name of the property) to this file. Users also set the value of
the property to IEEE_FP to indicate that they wanted IEEE floating-point values passed to their
JNI code or TANDEM_FP to indicate that they wanted TNS floating-point values passed to their JNI
code.
A user program cannot specify the floating-point type by using the
TandemVMClassFP.properties file. Thus, any user-program or Java based product with JNI
code that obtains floating-point values from Java must call the NSK_FLOAT_* Guardian routines
to convert these values to TNS floats. Likewise, any float value passed to Java must be an IEEE
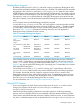
float value. Table 11 (page 83) illustrates the NonStop Server for Java 6.0 application’s
floating-point usage compared to earlier versions.
Table 11 Summary of Floating Point Support
NSJ 6.0NSJ 5.xNSJ 4.xNSJ 3.xNSJ 2.x
IEEE floatIEEE floatIEEE floatIEEE floatIEEE floatJava
floating-point
usage
IEEE floatIEEE floatIEEE floatEither IEEE or
Tandem float
Either IEEE or
Tandem float
JNI code floating
point
IEEE floatIEEE floatIEEE floatEither IEEE or
Tandem float
Tandem floatJNI calling
convention
IEEE floatIEEE floatIEEE floatIEEE floatTandem floatJava compiler
flag
IEEE floatIEEE floatIEEE floatTandem floatTandem floatJava linker flag
Since NonStop Server for Java 3.1.x and earlier set the linker flag for the process to TNS float,
any use of the C runtime library used routines that handled TNS floats. For NonStop Server for
Java 4 , 5, 5.1, and 6.0 versions, the linker flags described under “Linker and Compiler Options”
(page 45) are used to specify IEEE floating point. Accordingly, the C runtime library uses routines
that handle IEEE floating point.
For NonStop Server for Java 4 , 5, 5.1, and 6.0 versions, any C runtime library calls such as
sprintf or sscanf, made from JNI code, assumes IEEE float values and calling conventions.
For example, assume that JNI code, written for a previous version of Java, converts a TNS
floating-point value to a string, which is then passed to Java. To migrate the program, you must
change the JNI code to convert the TNS floating-point value to an IEEE floating-point value and
then call sprintf to convert the floating-point value to a string.
For more information, see “IEEE Floating-Point Implementation” (page 46).
Using AWT Classes
If your Java programs use AWT classes with NonStop Server for Java 3.1.x or earlier versions,
change your program code to catch a HeadlessException rather than an
UnsupportedClassException.
Because the NonStop operating system does not provide support for windowing operations,
previous versions of NonStop Server for Java supported only those Abstract Windowing Toolkit
(AWT) classes and methods that did not require a display, keyboard, sound, or mouse operation.
Any class or method that required such an operation threw an UnsupportedClassException.
Floating-Point Support 83