SmartSetup Scripting Toolkit Deployment Guide for HP Integrity Servers with Microsoft Windows Server 2003 for Itanium-based Systems
Table Of Contents
- SmartSetup Scripting Toolkit Deployment Guide
- Table of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 Overview
- 2 Creating a server profile
- 3 Setting up the toolkit environment
- 4 Setting up the boot mechanism
- Using a bootable CD/DVD
- Using a USB flash device
- Using network boot
- Interrupting the SSTK deployment process
- 5 Utilities Reference
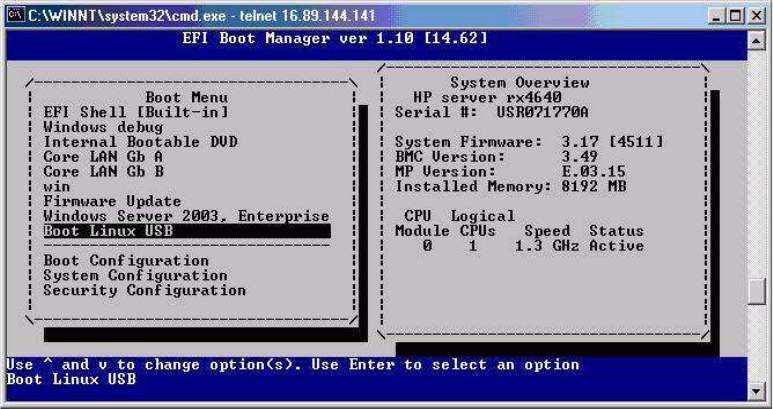
Figure 4-10 Boot from Linux USB Device Window
Using USB flash device as external media
Assuming the USB device is /dev/sda you can mount your MS-DOS formatted USB device
using:
mount –t msdos /dev/sda /mnt
Using network boot
The following sections show you how to set up a network boot environment using a Windows
system or a Linux system.
Setting up a Windows network boot server
The DHCP server leases dynamic IP addresses. An extension to the DHCP protocol, PXE, allows
a system to boot from an initial OS image bootstrap program downloaded from a TFTP server.
To boot a remote OS image:
1. The client machine boots with a NIC as the first boot device.
2. The NIC client issues a DHCP DISCOVER.
3. The server replies with a DHCP OFFER. Along with the network configuration information,
the server sends information regarding the file to be downloaded by the client:
• The TFTP server from which the file has to be downloaded.
• The file name bootia64.efi, calls elilo.efi.
4. The NIC downloads the image file from the TFTP server executes it.
5. The elilo.efi utility automatically gets its configuration file (usually elilo.conf) from
the remote TFTP server.
6. The elilo.efi utility parses the configuration file, downloads the kernel image and initrd
file (optional) from the TFTP server and starts the boot process.
Setting up a TFTP server
The role of the TFTP server is to provide access to all the files required during the boot process.
Copy the files in the boot_files\efi\boot directory of the repository to the root directory
of the TFTP server or to the path specified in the bootfile name configuration of the DHCP server.
The TFTP server must be listening to the default TFTP port (69).
48 Setting up the boot mechanism