SmartSetup Scripting Toolkit Deployment Guide for HP Integrity Servers with Microsoft Windows Server 2003 for Itanium-based Systems
Table Of Contents
- SmartSetup Scripting Toolkit Deployment Guide
- Table of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 Overview
- 2 Creating a server profile
- 3 Setting up the toolkit environment
- 4 Setting up the boot mechanism
- Using a bootable CD/DVD
- Using a USB flash device
- Using network boot
- Interrupting the SSTK deployment process
- 5 Utilities Reference
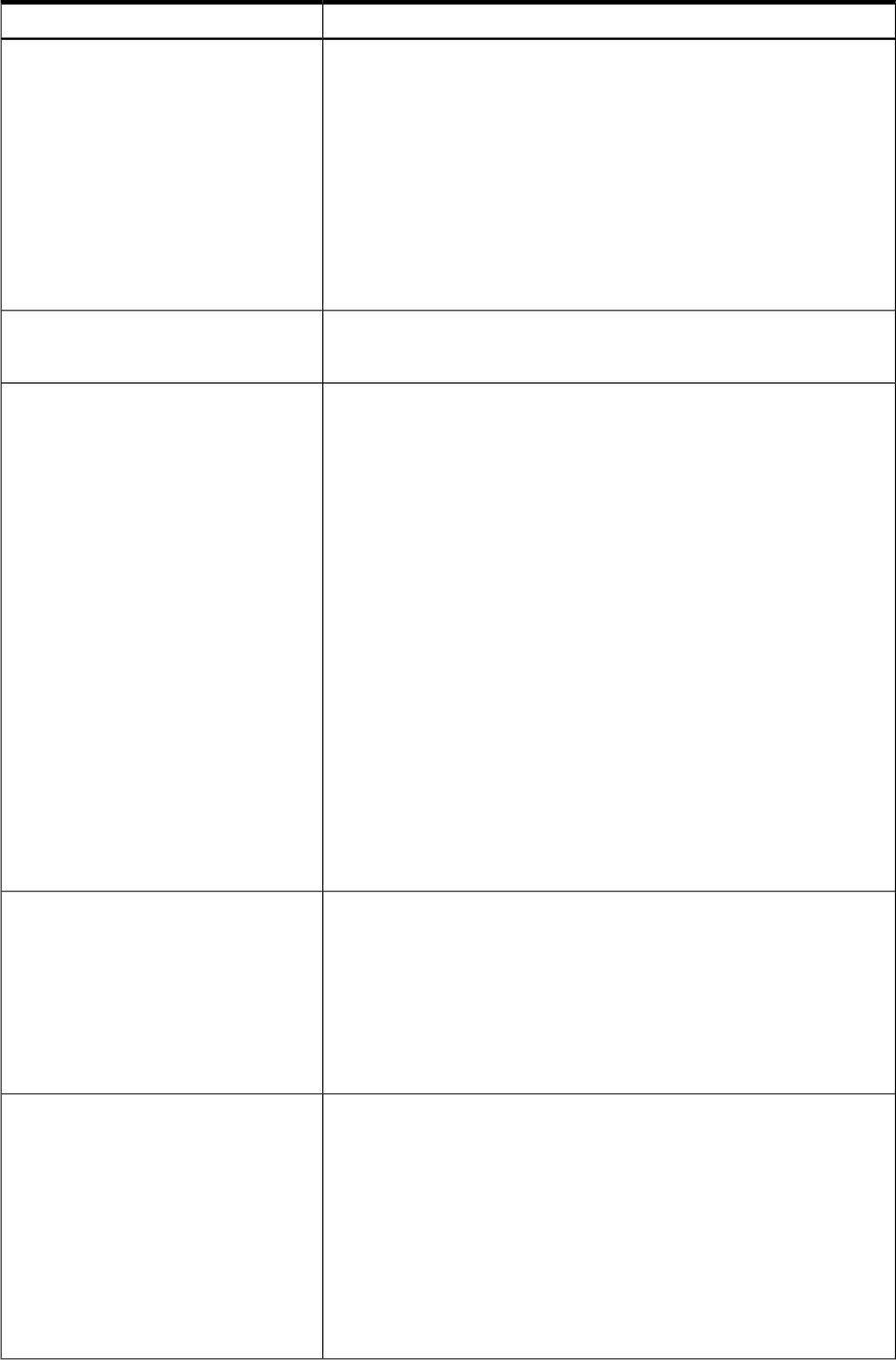
Table 5-5 Custom script file options
ValueOption
Defines if you are changing existing arrays and logical drives or adding
new ones. This option is required.
Configure: Existing arrays are not modified. Only new arrays and new
logical drives can be created in this mode.
Reconfigure: Existing arrays and logical drives might be modified in a
non-data-destructive manner. You can create new arrays, expand existing
arrays, create new logical drives, migrate existing logical drives, and extend
existing logical drives
If the -i-with-reset or -reset command line switch is used, the
existing controller configuration is cleared with data loss as the first step
in the configurations process, regardless of the setting of the Action mode.
Action
Defines if you are in Automatic or Custom mode.
Specify Custom for a custom script.
Method
Identifies to which controllers to apply the configuration. This option is
required.
Slot [N][:N]: The internal controller with slot number N is used.
External controllers can be identified by appending the Port Number. For
example, an MSA1500 connected to a SA6402 might be found at “Slot 4:2,”
where 4 is the internal Slot number and 2 is the SCSI port.
WWN [N]: The external controller with World-Wide Name (WWN) N is
used.
SerialNumber [N]: The shared storage controller with serial number
N is used.
All: All detected internal and external controllers in the system are used.
First: The first controller found, based on the controller with the lowest
PCI slot number.
IOCabinet [N], IOBay [N], IOChassis [N],Slot [N],
Cabinet [N], Cell [N]: The controller identified by the IPF Slot path
information is used.
Use of the -internal” and -external command line switches influences
what is regarded as the first controller. For example, if the -external
switch is used, the first controller will be the first external controller
discovered, regardless of the number of internal controllers in the host
system.
Controller
Specifies if the configuration should be cleared. This option causes data
loss since it deletes all logical drives on the controller. Other scripting
commands can exist after this option to recreate a new configuration. This
option is optional.
Yes: The configuration is cleared. All arrays and logical drives on the
controller are deleted.
No: The configuration is not cleared. This is the default option if the
command is not specified in the script file
ClearConfigurationWithDataLoss
Specifies the RaidArrayID for controllers that support RaidArrayID. This
is a user-defined string to identify controllers. Currently, RaidArrayIDs
are only supported by Fibre and shared-storage controllers.
“XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX”
Varying length string that can consist of any of the following characters:
a-z, A-Z, 0-9, ! @ # * ( ) , - _ + : . / [space]
This string has a maximum length that varies depending on the type of
controller. For, RA4x00 controllers, the max length is 24 characters. For,
other controllers, the max length is 20 characters. The quotes surrounding
the string are optional. Using quotes allows leading space characters to
be used in the RaidArrayID. This string cannot end in a space character.
RAIDArrayID
cpqacuxe 61










