HP Integrity rx7620 Server - User Service Guide, Sixth Edition
Cells and nPartitions
NOTE: In the following discussion, the term “cell” refers to a cell board.
A cell board that has an I/O link to a bootable device and a console (usually supplied by an
MP/SCSI core I/O card) is a potential boot cell. The cell that contains the boot console I/O path
is the called the root cell. Both cells are potential root cells. The primary or default root cell in a
single nPartition system is the bottom cell (cell 1).
An nPartition (also called a protection domain) is a cell or cells running the same operating
system and sharing processes and memory space among the components. Each nPartition must
have one root cell and may have both. The HP Integrity rx7620 Server has only two possible
nPartition configurations: single or dual. The additional cell that can be part of the nPartition
does not require I/O links or MP/SCSI core I/O cards.
In the single nPartition case, if two cells are present, either cell may be the root cell, assuming
that both cells have MP core I/O functionality present. If only one cell is present, that cell is the
root cell (and should be cell 1).
In the dual nPartition case (two cells required), each nPartition consists of one cell, and each cell
must be a root cell. The ability to interconnect two cells in one nPartition or isolate the cells in a
dual nPartition system provides system configuration flexibility. System partitioning is configured
by the system Management Processor (MP).
NOTE: Partition configuration information is available on the HP website at http://docs.hp.com.
For nPartitions details, see the HP System Partitions Guide: Administration for nPartitions.
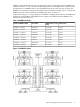
Internal Disk Devices for the HP Integrity rx7620 Server
In an HP Integrity rx7620 Server, the top internal disk drives connect to cell 1 through the core
I/O for cell 1. Both of the bottom disk drives connect to cell 0 through the core I/O for cell 0.
The CD/DVD/DAT drive connects to cell 1 through the core I/O card for cell 1.
Figure 1-10 Internal Disks
26 Introduction