HP Matrix 7.2 KVM Private Cloud Backup and Restore
Table Of Contents
- Abstract
- Matrix Operating Environment with Matrix KVM Private Cloud Overview
- Backup and restore strategy for Matrix OE with Matrix KVM Private Cloud
- Matrix KVM Private Cloud backup and restore
- Matrix KVM Private Cloud Images repository backup and restore
- Matrix KVM Private Cloud High Availability (HA) cluster configuration backup and restore
- Appendix A: KVM Private Cloud restore resynchronization actions
- Appendix B: Images repository restore resynchronization actions
- Appendix C: Alerts and Audit messages
- Appendix D: HA Cluster details
- Appendix E: Backup and Restore REST API
- Appendix F: Sample Backup Script
- Appendix G: Sample Restore Script
- References
- For more information
deploy, easy to use solution focused on the provisioning, optimization and ongoing management of infrastructure
services. It targets private, public and hybrid cloud solutions deployed by enterprise and service providers.
Optionally, the Matrix KVM Private Cloud can be run in an HA configuration, in a two-node cluster, to make it highly
available.
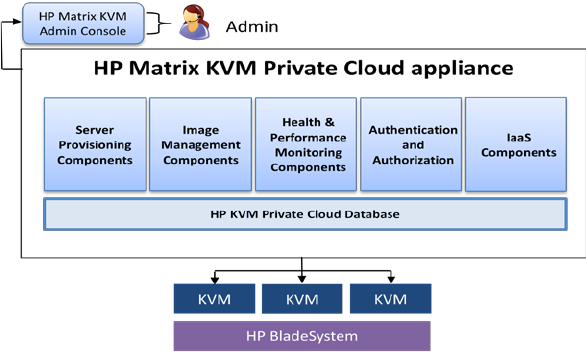
Matrix KVM Private Cloud Management Overview
HP Matrix KVM Private Cloud enables provisioning and on-going management of the KVM infrastructure with
significant focus on ease of deployment, ease of use and high scalability. It is built on OpenStack with services for
server provisioning, image management, health and performance monitoring, authentication and authorization and
other appliance specific IaaS components. The HP Matrix KVM Private Cloud appliance helps index, manage and
monitor various infrastructure resources, while providing events, alerts and recovery services for the KVM Private
Cloud.
Matrix KVM Private Cloud HA solution overview
The KVM Private Cloud appliance (ISC VM) runs as a virtual machine deployed on a KVM host. The VM HA solution
is based on a two-node cluster using an active-standby configuration. The ISC VM runs as a resource in a cluster
service on the active node. The cluster software monitors the health of the node and the virtual machine, and can
restart the virtual machine locally, or move it (fail over) to the standby node within the cluster when a failure is
detected. Administrators can also manually relocate the virtual machine appliance to the standby node, for example,
to allow the hypervisor host to be shut down for planned maintenance.
4










