Understanding and Designing Serviceguard Disaster Recovery Architectures
Using Alternative Power Sources
In a high-availability environment, redundancy is applied to cluster components, such as PV links,
redundant network cards, power supplies, and disks. In disaster recovery architectures another
level of protection is required for these redundancies.
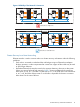
The power supply for each data center that houses part of a disaster recovery cluster must be from
a different circuit. In addition to a standard UPS (Uninterrupted Power Supply), each node in a
disaster recovery cluster must be on a separate power circuit, as shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5 Alternative Power Sources
Node 1
Node 2
Node 3
Node 4
Disk ArrayDisk Array
Data Center A
Power Circuit 1
Power Circuit 2
Power Circuit 3
Power Circuit 4
Data Center B
Housing remote nodes in another building often implies they are powered by a different circuit.
However, it is important to make sure that all nodes are powered from a different source if the
disaster recovery cluster is located in two data centers in the same building. Some disaster recovery
designs also ensure that their redundant power source is supplied by a different power substation
on the grid. This adds protection against large-scale power failures, such as brown-outs, sabotage,
or electrical storms.
Creating Highly Available Networking
Standard high-availability guidelines require redundant networks. Redundant networks may be
highly available, but they are not disaster recovery if a single accident can interrupt both network
connections. For example, if you use the same trench to lay cables for both networks, you do not
have a disaster recovery architecture because a single accident, such as a backhoe digging in
the wrong place, can sever both cables at once, making automated failover during a disaster
impossible.
In a disaster recovery architecture, the reliability of the network is paramount. To reduce the
possibility of a failure in both networks because of a single accident , redundant network cables
must be installed so that they use physically different routes for each network as indicated in
Figure 6. How you route cables depend on the networking technology you use. Specific guidelines
for some network technologies are listed here.
14 Disaster Recovery in a Serviceguard Cluster