R2511-HP MSR Router Series Voice Configuration Guide(V5)
5
O
p
eration Reference
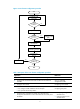
6. Configure number application for the dial plan adopted in the network
diagram.
Configuring dial plans
7. Configure the following voice protocols according to the service and
networking environment:
{ H.323 protocol
{ SIP protocol
{ Fax protocol
• Configuring H.323
• Configuring SIP
• Configuring fax over IP
8. Check whether the network requirements are met:
{ If so, the configuration is completed.
{ If not, check the fault and perform re-configuration.
N/A
Voice subscriber lines
Voice subscriber lines, which are connected to telephone network devices such as analog telephone and
PBX, implement all physical layer functions between VoIP gateways and PSTN devices. These functions
include power supply to analog telephones, off-hook state detection, ringing signal generation, receiving
& sending of analog or digital voice calls, and receiving & sending of dialed digits for call routing.
For more information about the voice subscriber line, see "Configuring analog voice subscriber lines"
and "Configuring digital voice subscriber lines." The router provides the following voice subscriber lines:
• FXS analog voice subscriber line, corresponding to an FXS interface. FXS analog voice subscriber
lines are usually connected to FXO subscriber line terminals, such as ordinary analog telephones,
to provide ringing current, ringing voltage, and dial tone.
• FXO analog voice subscriber line, corresponding to an FXO interface or 2-port loop trunk interface.
FXO analog voice subscriber lines are usually connected to analog telephone interfaces of PSTN
central offices (PBXs).
• E&M analog voice subscriber line, corresponding to an E&M interface. E&M analog voice
subscriber lines support analog E&M signaling and divide each voice connection into a trunk circuit
side and a signaling unit side (similar to the relationship between DCE and DTE). PBXs send signals
to routers through M lines and receive signals from routers through E lines.
• Digital E1/T1 voice subscriber line, that is, a TS set or PRI group created on a VE1/VT1 interface
card. After a TS set or PRI group and signaling types, such as R2 signaling, digital E&M signaling,
or digital LGS are configured on VE1/VT1 voice interface cards, the system will automatically
generate the corresponding voice subscriber line for the TS set or PRI group. If a TS set is created,
the E1/T1 interface supports R2, digital E&M, and digital LGS signaling. If a PRI group is created,
the E1/T1 interface supports ISDN, where DSS1 and QSIG are commonly used protocol types.
• BSV voice subscriber line, which supports ISDN. Generally, a BSV interface is used to connect an
ISDN digital telephone, or used as a trunk interface to connect a PBX digital trunk.
Voice entities
For information about voice entity configuration, see "Configuring voice entities", "Configuring VoFR",
and "Configuring customizable IVR."
There are four kinds of voice entities: POTS entity, VoIP entity, VoFR entity, and IVR entity.