HP MSR2000/3000/4000 Router Series IP Multicast Configuration Guide
42
4. Configure a static multicast route on Router B, specifying Router C as its RPF neighbor to the
source.
[RouterB] ip rpf-route-static 50.1.1.100 24 20.1.1.2
Verifying the configuration
# Use the display multicast rpf-info command on Router B to display information about the RPF route to
the source.
[RouterB] display multicast rpf-info 50.1.1.100
RPF information about source 50.1.1.100:
RPF interface: Ethernet1/2, RPF neighbor: 20.1.1.2
Referenced route/mask: 50.1.1.0/24
Referenced route type: multicast static
Route selection rule: preference-preferred
Load splitting rule: disable
The output shows the following:
• The RPF route on Router B is the configured static multicast route.
• The RPF neighbor of Router B is Router C.
Creating an RPF route
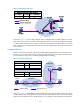
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 19, PIM-DM runs in the network and all routers in the network support IP multicast.
Router B and Router C run OSPF, and have no unicast routes to Router A. Typically, the receiver host
receives the multicast data from the source 1 in the OSPF domain.
Perform the configuration so that the receiver host can receive multicast data from the source 2, which is
outside the OSPF domain.
Figure 19 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
1. Configure the IP address and subnet mask for each interface as shown in Figure 19. (Details not
shown.)