HP MSR2000/3000/4000 Router Series Layer 2 - WAN Configuration Guide
38
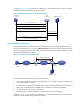
Figure 22 Establishment process for LAC-auto-initiated tunnels
L2TP features
• Flexible identity authentication mechanism and high security—L2TP by itself does not provide
security for connections. However, it has all the security features of PPP and allows for PPP
authentication (CHAP or PAP). L2TP can also cooperate with IPsec to guarantee data security,
strengthening the guard against attacks for tunneled data.
• Multiprotocol transmission—L2TP tunnels PPP frames, which can be used to encapsulate packets of
multiple network layer protocols.
• RADIUS authentication—An LAC or LNS can send the username and password of a remote user to
a RADIUS server for authentication.
• Private address allocation—An LNS can dynamically allocate private addresses to remote users,
facilitating corporate private address management (RFC 1918) and improving security.
• Flexible accounting—Accounting can be simultaneously carried out on the LAC and LNS, allowing
bills to be generated on the ISP side and charging and auditing to be processed on the enterprise
gateway. L2TP can provide accounting data, such as inbound and outbound traffic statistics (in
packets and bytes) and the connection's start time and end time. The AAA server uses this data for
flexible accounting.
• Reliability—L2TP supports LNS backup. When the connection to the primary LNS is torn down, an
LAC can establish a new connection to a secondary LNS. This redundancy enhances the reliability
of L2TP services.
• Issuing tunnel attributes by RADIUS server to LAC—In NAS-initiated mode, the tunnel attributes can
be issued by the RADIUS server to the LAC. To receive these attributes, you only need to enable
L2TP and configure remote AAA authentication for PPP users on the LAC.
When an L2TP user dials in to the LAC, the LAC as the RADIUS client sends the user information to
the RADIUS server. The RADIUS server authenticates the PPP user, returns the result to the LAC, and
issues L2TP tunnel attributes for the PPP user to the LAC. The LAC then sets up an L2TP tunnel and
sessions based on the issued L2TP tunnel attributes.
(1) Tunnel setup request
(2) CHAP authentication (challenge/response)
(4) LCP negotiation and user authentication
(5) Access request
(6) Acesss accept
(7) Authentication passes, and assign an IP
address
LAC
Device A
LNS
Device B
RADIUS server
Remote system
Host A
(8) Access the enterprise network
(3) Setup a session