R0106-HP MSR Router Series Layer 2 - LAN Switching Configuration Guide(V7)
12
Configuring Ethernet link aggregation
Ethernet link aggregation bundles multiple physical Ethernet links into one logical link, called an
aggregate link. Link aggregation has the following benefits:
• Increased bandwidth beyond the limits of any single link. In an aggregate link, traffic is distributed
across the member ports.
• Improved link reliability. The member ports dynamically back up one another. When a member
port fails, its traffic is automatically switched to other member ports.
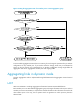
As shown in Figure 1, Device A and Device B are connected by three physical Ethernet links. These
ph
ysical Ethernet links are combined into an aggregate link called link aggregation 1. The bandwidth of
this aggregate link can be as high as the total bandwidth of the three physical Ethernet links. At the same
time, the three Ethernet links back up one another. When a physical Ethernet link fails, the traffic
previously carried on the failed link is switched to the other two links.
Figure 1 Ethernet link aggregation diagram
NOTE:
In this chapter, "MSR2000" refers to MSR2003. "MSR3000" collectively refers to MSR3012, MSR3024,
MSR3044, MSR3064. "MSR4000" collectively refers to MSR4060 and MSR4080.
Basic concepts
Aggregation group, member port, and aggregate interface
Link bundling is implemented through interface bundling. An aggregation group is a group of Ethernet
interfaces bundled together, which are called member ports of the aggregation group. For each
aggregation group, a logical interface (called an aggregate interface), is created. To an upper layer
entity that uses the link aggregation service, a link aggregation group appears the same as a single
logical link and data traffic is transmitted through the aggregate interface.
When you create an aggregate interface, the device automatically creates an aggregation group of the
same type and number as the aggregate interface. For example, when you create aggregate interface
1, aggregation group 1 is created.
Aggregate interfaces include Layer 2 aggregate interfaces and Layer 3 aggregate interfaces.
You can assign Layer 2 Ethernet interfaces only to a Layer 2 aggregation group, and Layer 3 Ethernet
interfaces only to a Layer 3 aggregation group.
On a Layer 3 aggregate interface, you can create subinterfaces.
The port rate of an aggregate interface equals the total rate of its Selected member ports. Its duplex
mode is the same as that of the Selected member ports. For more information about the states of member
ports in an aggregation group, see "Aggregation states of member ports in an aggregation group."