R0106-HP MSR Router Series Layer 2 - LAN Switching Configuration Guide(V7)
42
permits too many VLANs, both resources and calculations for maintaining the VLAN spanning trees
increase dramatically. If a status change occurs to the trunk or hybrid port that permits multiple
VLANs, the device CPU will be overburdened with recalculating the affected spanning trees. As a
result, network performance is degraded.
MSTP features
Developed based on IEEE 802.1s, MSTP overcomes the limitations of STP, RSTP, and PVST. In addition to
supporting rapid network convergence, it allows data flows of different VLANs to be forwarded along
separate paths. This provides a better load sharing mechanism for redundant links.
MSTP provides the following features:
• MSTP divides a switched network into multiple regions, each of which contains multiple spanning
trees that are independent of one another.
• MSTP supports mapping VLANs to spanning tree instances by means of a VLAN-to-instance
mapping table. MSTP can reduce communication overheads and resource usage by mapping
multiple VLANs to one instance.
• MSTP prunes a loop network into a loop-free tree, which avoids proliferation and endless cycling of
packets in a loop network. In addition, it supports load balancing of VLAN data by providing
multiple redundant paths for data forwarding.
• MSTP is compatible with STP and RSTP, and partially compatible with PVST.
MSTP basic concepts
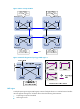
Figure 12 shows a switched network that comprises four MST regions, each MST region comprising four
MSTP devices. Figure 13 sho
ws the networking topology of MST region 3.