R0106-HP MSR Router Series Layer 3 - IP Services Configuration Guide(V7)
89
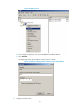
Figure 33 Network diagram
Configuration procedure
# Configure a mapping between host name host.com and IP address 10.1.1.2.
<Sysname> system-view
[Sysname] ip host host.com 10.1.1.2
# Use the ping host.com command to verify that the device can use static domain name resolution to
resolve domain name host.com into IP address 10.1.1.2.
[Sysname] ping host.com
Ping host.com (10.1.1.2): 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=255 time=1.000 ms
56 bytes from 10.1.1.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=255 time=2.000 ms
--- Ping statistics for host.com ---
5 packet(s) transmitted, 5 packet(s) received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/std-dev = 1.000/1.200/2.000/0.400 ms
Dynamic domain name resolution configuration example
Network requirements
As shown in Figure 34, the device wants to do the following:
• Access the host by using an easy-to-remember domain name rather than an IP address.
• Ask the DNS server on the network for an IP address by using dynamic domain name resolution.
The IP address of the DNS server is 2.1.1.2/16 and the DNS server has a com domain, which stores the
mapping between domain name host and IP address 3.1.1.1/16.
Configure dynamic DNS and the DNS suffix com on the device that serves as a DNS client. The device
can then use the domain name host to access the host with the domain name host.com and the IP
address 3.1.1.1/16.
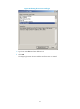
Figure 34 Network diagram