Availability Guide for Application Design
Data Protection and Recovery
Availability Guide for Application Design—525637-004
4-17
Remote Duplicate Transactions
When Transaction Logic Executes in the Server
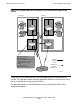
Figure 4-5 shows a similar scheme with the transaction logic running in the server.
New York has the primary system. Again, the backup system is located in Chicago.
Here, TMF operates remotely to keep the backup and primary databases
synchronized. The server on the backup system is not used in normal operation.
How Do These Approaches Compare With Using the RDF
Approach?
As with the RDF approach, both of these approaches provide an up-to-date, consistent
database even following environmental disaster, because the databases are kept in
geographically remote locations. Switchover time, however, is minimized. The
disadvantage is extra code execution in the switching system to send the information
Figure 4-5. Remote, Duplicate Transactions With the Logic in the Server
Network
New
York
$DBNY
$AUDIT
Chicago
$DBNY
$AUDIT
Read Inbound Packet
Begin Transaction
Write to Database in New
York
Write to Database in Chicago
End Transaction
Write Outbound Packet
Normal
Data
Flow
Alternate
Data
Flow
Server
Server
VST305.vdd