Availability Guide for Application Design
Data Protection and Recovery
Availability Guide for Application Design—525637-004
4-20
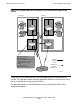
Using Queue Files
•
The term trickle catchup describes a technique that can be used in applications
where the order of requests must be maintained.
Queue files are a generic concept. For details on how to write programs using a
specific implementation, refer to the Queue Manager Manual.
Using Queue Files
Using the Queue Manager, processes enqueue and dequeue messages from queue
files using the following operations:
•
The ENQ operation enables a process to enqueue a message on a queue file.
•
The DEQ operation enables a process to dequeue a message from a queue file. If
no message is there, the operation returns with an empty queue indication.
•
The WAITQ operation enables a process to listen for messages arriving on a
queue. The operation returns only when there is a message for the process to
read. The process then issues a DEQ operation to dequeue the message.
•
The READQ operation allows a process to read an entry from a queue without
deleting the entry. If no message is there, the operation returns with an empty
queue indication.
Queue File Records Can Be Transaction-Protected
Protection against outages is achieved through mirrored disks and transaction
protection. You can protect queue files against media failure simply by using mirrored
disks.
For protection against system failure, the file must be audited. To enqueue records to
an audited queue file, your processes must enclose the enqueue operations within
begin-transaction and end-transaction statements. If the process aborts the
transaction, all records written within that transaction are removed from the queue.
Similarly, if a system failure occurs while the transaction is executing, volume recovery
is performed to dequeue any records that were written by uncommitted transactions
before the failure occurred.
Similarly, when dequeueing records from an audited queue file, the dequeue
operations must be enclosed within begin-transaction and end-transaction statements.
If the transaction aborts or system failure occurs within the transaction, the dequeued
records are automatically written back into the file.
Transaction Playback
Consider an application in which a client process runs on a local system whose
purpose is to route requests from point-of-sale devices to services on remote server
systems. If a remote server system that provides the only instance of a given service
becomes unavailable, then the application also becomes unavailable because the
required service is lost.