Availability Guide for Application Design
Overview of Server and Network Fault Tolerance
Availability Guide for Application Design—525637-004
2-2
Fault Tolerance in the Server System
This is only true of a TNS/R or TNS/E duplex system, if you are using a triplex system
based on the new NonStop advanced architecture of the HP Integrity NonStop
NS-series servers then you will have two fault-tolerant levels of protection.
When a similar failure occurs on equipment from most other vendors, an outage
typically occurs. The failed component must be repaired to get the application back
online.
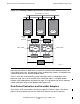
Figure 2-1 compares component failure in a HP server with component failure in
equipment supplied by a typical alternate vendor. The HP server continues to operate
with a reduced level of fault tolerance. The other vendor’s system is down.
Wide area networks of HP systems have long been designed to detect and recover
from loss of lines through the use of advanced protocols provided by the Expand
product. The ServerNet product extends this concept to all communication paths within
an S-series system. The NonStop Access for Networking product optionally extends
this concept into local area networks (LANs) from D-series systems, enabling
automatic and transparent recovery from component failure of an Ethernet LAN
controller, router, hub, or LAN cable.
Fault Tolerance in the Server System and Fault Tolerance in a Client/Server Network
on page 2-17 provide overviews of how fault tolerance is achieved.
Fault Tolerance in the Server System
The HP NonStop series is designed around the concept that it is possible to build a
system that is an order of magnitude more reliable than the components it is made of.
Exploiting its parallel architecture, it is possible to eliminate single points of failure and
hence increase the availability of the entire system to a level many times that of any
individual component.
Modern technology endows components with impressive reliability statistics often
quoted as the mean time between failures (MTBF). These numbers have lead to the
misconception that fault tolerance involving redundant components is unnecessary.
Figure 2-1. Fault Tolerance and Availability
Fault-Tolerant
Not Fault-
Tolerant
HP
Other Vendor
Outage
Component
Failure
Repair
Not Fault-
Tolerant
Component
Failure
Repair
VST201.vdd