Availability Guide for Application Design
Overview of Server and Network Fault Tolerance
Availability Guide for Application Design—525637-004
2-19
Benefits of a Continuously Available Server
•
Duplicate network addresses, such as duplicate IP addresses, are on the same
network.
•
A virus is spreading across network nodes.
•
A name/security server is hung, or the database is incorrect.
•
Operations stopped the application.
•
A network-wide router reset has occurred.
Many of these problems can be avoided by using the right hardware and application
design. All can have their effects minimized. The remainder of this subsection shows
some hardware design techniques that help. Section 5, Increasing the Availability of
Tuxedo Applications, and Section 6, Availability in the Pathway Transaction-Processing
Environment, provide some hints on minimizing these problems by appropriate
application design.
Benefits of a Continuously Available Server
Sixty percent of downtime of a typical client/server application is caused by server
problems. Clearly, the most significant ways to reduce downtime are to:
•
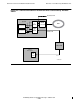
Use a continuously available (HP) server as shown in Figure 2-6 on page 2-20 and
Figure 2-7 on page 2-21.
•
Design your client/server application to run continuously, as described in this
manual.
•
Manage problems that arise to eliminate outages.
•
Manage reconfiguration without bringing the application down.
An S-series or NS-series system provides the necessary redundancy for fault-tolerant
network access through:
•
Primary and backup connections between the ServerNet fabrics and the Ethernet 4
ServerNet adapter and Gigabit Ethernet ServerNet Adapters (GESA) for both:
°
A dedicated LAN supporting the ServerNet Wide Area Network (SWAN)
converter for WAN connections
°
A public LAN, accessed through a network hub
•
Primary and backup access ports between the SWAN converter and its dedicated
LAN.
A K-series system provides the necessary redundancy for fault-tolerant network
access through its dual-ported LAN controller.