Availability Guide for Application Design
Overview of Server and Network Fault Tolerance
Availability Guide for Application Design—525637-004
2-22
Use Fault-Tolerant Clients
Single-point failure of any of these components is tolerated. Rapid fault detection and
reporting ensures that the repair can take place as quickly as possible, thereby
minimizing the repair window during which the LAN is not fault-tolerant.
Use Fault-Tolerant Clients
Fault-tolerant clients can provide some additional protection. These PCs protect
against most PC hardware failures including disk and power failures. However, they do
not currently protect against software failures or allow online reconfiguration.
An alternative to fault-tolerant PCs is to have standby PCs available. Such an
approach can provide hardware and software fault tolerance in some applications.
Use Fault-Tolerant Network Services
The final step to a fault-tolerant LAN is to provide fault-tolerant network services to
your client workstations. High-level services such as domain name service (DNS)
servers can be replicated in multiple processors. Services such as remote server call
(RSC/MP) server processes can be run as persistent processes. On HP systems, fault-
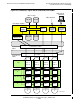
Figure 2-8. An S-Series Fault-Tolerant LAN
Processor 0
Processor 1
HP Server
System
Adapter
Card
Client
Processor
Network Hub Network Hub
E4SA
or
GESA
Primary LAN
Backup LAN
VST208.vdd