Availability Guide for Application Design
Overview of Server and Network Fault Tolerance
Availability Guide for Application Design—525637-004
2-23
The HP Integrity NonStop NS-Series Server
Provides Another Level of Availability
tolerance is built into HP network service products at all levels of the OSI layer model,
as shown in the next subsection.
Section 6, Availability in the Pathway Transaction-Processing Environment, discusses
techniques for replicating server processes. Section 7, Availability Through Process-
Pairs and Monitors, discusses techniques for creating persistent and NonStop
processes.
The HP Integrity NonStop NS-Series Server
Provides Another Level of Availability
This architecture is known as the NonStop advanced architecture (NSAA). At the
highest level, the basic building block of a NonStop NS-series system is the processor
complex. A processor complex consists of two or three CPU modules called processor
slices in NSAA. Each slice houses two or four microprocessors called processor
elements. A logical processor consists of one processor element from each slice.
Although a logical processor physically consists of multiple processor elements, with
each element contained in a separate enclosure, it is convenient to think of a logical
processor as a single entity within the system. Each logical processor has its own
memory and its own copy of the operating system and processes a single instruction
stream. Logical processors are usually referred to simply as “processors.”
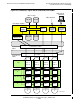
A processor complex consisting of three processor slices, as shown in Figure 2-9, NS-
Series Triplex Server Attached to ServerNet, on page 2-24 is referred to as a triplex, or
triple modular redundancy (TMR), system. A duplex, or double modular redundancy,
configuration (two processor slices) is also available. In a duplex or triplex
configuration, the system can continue to function in the event of failure of a processor
element. The failed component within a slice, such as a processor element, power
supply, and so forth can be replaced while the system continues to run. This approach
provides fault tolerance not found in traditional architectures.
As you might expect, the triplex system provides additional fault tolerance over the
duplex system. If a slice should fail in a triplex system, one of the two remaining
functional slices takes over; the system becomes, in effect, a duplex system, with one
slice remaining as a backup.
A single NonStop NS-series system can have up to four processor complexes for a
total of 16 processors. Processors communicate with each other over dual ServerNet
fabrics.
A fabric is more complex than a bus. A bus has a straightline set of parallel conductors
with a start and end point. A fabric is a web of links between electronic routers that
provide a large number of possible paths from one point to another.
All input and output to and from each slice goes through a logical synchronization unit
(LSU). The LSU interfaces with the ServerNet fabrics and contains logic that compares
all output operations of a logical processor, ensuring that all slices agree on the result
before the data is passed to the ServerNet fabrics.