Availability Guide for Problem Management
Problem Management Tools
Availability Guide for Problem Management–125509
9-6
How Does EMS Collect, Filter, and Distribute Event
Messages?
How Does EMS Collect, Filter, and Distribute Event Messages?
There are two types of EMS processes that manage the flow of event messages from the
subsystem environment to the operations environment: event-message collectors and
event-message distributors. Collectors accept event messages from subsystems and log
them to a log file, and distributors filter event messages and return selected messages to
the operations environment.
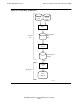
Figure 9-1 illustrates the flow of event messages in a system. Messages originate in the
subsystems and are then sent by the subsystems to the primary and alternate collector
processes. Collectors write event messages to the log files. Distributors retrieve selected
messages from the log files and send them to processes, printers, terminals, and other
destinations in the operations environment.
Event Message Collectors
EMS supports two types of event message collectors: a primary collector and alternate
collectors.
Primary Collector ($0)
Each system (or node) has only one primary event message collector, named $0. It is
configured during system generation and always runs as a NonStop process. $0 is the
primary collection point for all event messages generated by all reporting subsystems in
a system.
Alternate Collectors
Alternate collectors offer an alternative to the central collection point provided by the
primary collector, $0. Alternate collectors provide functions similar to those supplied by
$0, but each alternate collector maintains its own log files. The separation of events into
several log files speeds up event processing because a network management application
program does not have to read a single large file containing many events unrelated to
that application.
Log Files
The collectors write messages to event log or alternate log files, which allow you to
separate your system and application environments. The primary event log is maintained
by the primary collector ($0). Alternate collectors write messages to their own logs.
Applications have to explicitly send their events to specific alternate collectors to
maintain the separation of system and application messages.