CORBA 2.3.3 Administration Guide (NonStop CORBA 2.3.7+)
tsmp_server true
server_class NS
Changing an Entity
To change an entity, type the entity name followed by an open brace. This command causes subsequent lines to
modify the entity. Each line contains a single key and its associated value. A closing brace terminates data entry.
When an input line contains a key that is the same as an existing key, the new value replaces the current value.
When an input line contains a new key, the new key and value are made part of the entity. For example, to change
the value of Fs_server for the entity displayed in the previous example, use this entity command:
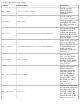
entity NS@ORB {
Fs_server false }
To remove a key and value from an entity, use the entitydeletekey command. For example, to delete the
key use_comm_server and its value from the NS@ORB entity, use this command:
entitydeletekey NS@ORB use_comm_server
Adding an Entity
To add an entity to the configuration database, use the first technique described in Changing an Entity. When you
use a new entity name, the subsequent keys and values define that entity. For example, the following entity
command would create a new entity named tcp_client@ORB:
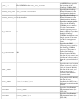
entity tcp_client@ORB {
tsmp_client false
Fs_client false }
Deleting an Entity
To delete an entity (along with its keys and values) from the configuration database, use the entitydelete
command. For example, to delete an entity named app_profile@ORB, use this command:
entitydelete app_profile@ORB
Exiting cfgmgt
When you are finished using cfgmgt, return to the OSS command prompt by entering one of the following
commands:
bye●
exit●
quit●
Managing NonStop CORBA Processes
The nsdstart script configures and starts the various processes that comprise the NonStop Services for
CORBA. These processes run under the Pathway environment that provides them with capabilities such as
auto-restart and scalability. After being started, the NonStop Services for CORBA are ready to receive and
process requests.