CRE Programmer's Guide
CRE Services
Common Run-Time Environment (CRE) Programmer’s Guide—528146-004
2-20
Sharing Standard Files Using the CRE
•
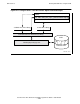
Figure 2-4 on page 2-22 shows the TAL routine opening standard output by calling
CRE_File_Open_. The path from TAL to the CRE is a solid line and, because this
is the first time a routine has requested a connection to standard output, the CRE
calls the system procedure FILE_OPEN_. The path to the operating system is a
solid line and the operating system box is shaded. When the call to FILE_OPEN_
completes, the CRE grants the TAL routine a connection to the file and returns the
connection number to the TAL routine.
•
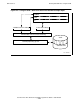
Figure 2-5 on page 2-23 shows the C routine opening standard output. Because
the main routine is not written in C, the C run-time library does not open standard
input, standard output, or standard log when your program begins execution.
Therefore, the C routine must call the fopen_std_file() library function for
each standard file that it accesses.
When the C routine calls fopen_std_file(), the C run-time library calls the
CRE to open standard output. The CRE does not call FILE_OPEN_ because the
CRE already has an open to $VOL.SUBVOL.FILE as a result of the preceding TAL
request. The CRE grants the C routine a connection to $VOL.SUBVOL.FILE and
returns the connection to the C run-time library. The operating system box in
Figure 2-5 on page 2-23 is not shaded because the CRE does not send an open
request to the operating system.
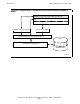
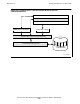
Figure 2-2. Using the CRE—Mixed-Language Process—Quiescent State
C Run-Time Library
203VST .VSD
$VOL
SUBVOL.FILE
0
1
2
3
COBOL:
TAL:
C:
COBOL Run-Time Library
NonStop Operating System
Common Run-Time Environment Library