CRE Programmer's Guide
CRE Services
Common Run-Time Environment (CRE) Programmer’s Guide—528146-004
2-23
Sharing Standard Files Using the CRE
Figure 2-6 through Figure 2-9 repeat the same sequence as shown in Figure 2-2
through Figure 2-5. In Figure 2-7 through Figure 2-9, however, a routine from each of
COBOL, TAL, and C writes a record to standard output.
•
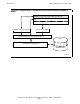
Figure 2-6 on page 2-24 shows a quiescent system. Standard output has been
opened by routines written in C and TAL.
•
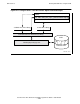
Figure 2-7 on page 2-25 shows the COBOL routine executing a DISPLAY verb to
write the letter A to standard output. Before calling the CRE to write the letter A,
the COBOL run-time library calls the CRE to open standard output. The CRE
grants a connection to the already open file and returns to the COBOL run-time
library, which writes the letter A to standard output. The letter A appears at the first
logical location in the file $VOL.SUBVOL.FILE.
•
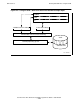
Figure 2-8 on page 2-26 shows a TAL routine writing a record to standard output.
Although this is the first TAL write to standard output, its record, containing the
letter B, is written to the second record of standard output.
•
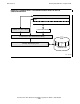
Figure 2-9 on page 2-27 shows a C routine writing a record to standard output.
Although this is the first C write to standard output, its record, containing the letter
C, is written to the third record of standard output.
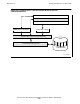
Figure 2-5. Using the CRE—The C Routine Opens Standard Output
COBOL:
TAL:
C: fopen_std_file(STDOUT, FALSE);
C Run-Time Library
206VST .VSD
$VOL
SUBVOL.FILE
0
1
2
3
COBOL Run-Time Library
NonStop Operating System
Common Run-Time Environment Library