Data Transformation Engine Type Designer Reference Guide
Chapter 9 - Partitioning Introduction to Partitioning
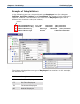
The following is an example of partitioning to simplify rules. The example
compares the differences between rules needed with and without partitioning. In
the rule without partitioning, you would specify a condition for each state
abbreviation in each region. This could make your mapping rules long, difficult to
read, and difficult to maintain. The mapping rule with partitioning is more concise,
self-documenting, and easier to maintain.
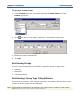
Map rule without partitioning:
=IF(ShipToCode Field:.:Input="NY"|
ShipToCode Field:.:Input="NJ"|
ShipToCode Field:.:Input="PA",
F_MapEast (Record:Input), NONE)
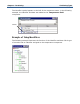
Map rule with partitioning:
=F_MapEast (EXTRACT (Record:Input,
PARTITION (ShipToCode Field:.:Input, East)))
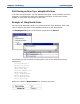
Benefits of Partitioning
Using the above example, explore the benefits of partitioning.
♦ The rule is shorter than the rule without partitioning. The knowledge of which
states belong to each region is maintained in the type tree rather than the map
rule.