Debug Manual
Table Of Contents
- What’s New in This Manual
- About This Manual
- 1 Introduction
- Execution Modes on TNS/R Systems
- What User Access Is Required for Debugging
- How to Make a Process Enter Debug
- How to Select Debug as the Debugger
- Why a Process Enters Debug
- How to Determine Process State on a Trap or Signal
- Ending a Debug Session
- What Appears in the Debug Header Message
- How to Use Debug
- How Debug Breakpoints Work
- 2 Using Debug on TNS/R Processors
- 3 Debug Command Overview
- 4 Debug Commands
- Command Summary
- A Command
- AMAP Command
- B Command
- BASE Command
- BM Command
- C Command
- CM Command
- D Command
- DJ Command
- DN Command
- EX[IT] Command
- F[ILES] Command
- FC Command
- FN Command
- FNL Command
- FREEZE Command
- HALT Command
- H[ELP] Command
- I Command
- IH Command (TNS/R Native and OSS Processes)
- INSPECT Command
- LMAP Command
- M Command
- MH Command (TNS/R Native and OSS Processes)
- P[AUSE] Command
- PMAP Command (Accelerated Programs)
- PRV Command
- R Command
- S[TOP] Command
- T Command
- V Command
- VQ Command
- VQA Command
- = Command
- ? Command
- A Error Messages
- B ASCII Character Set
- C Command Syntax Summary
- Register Syntax
- Expression Syntax
- Address Syntax
- A Command
- AMAP Command
- B Command
- BASE Command
- BM Command
- C Command
- CM Command
- D Command
- DJ Command
- DN Command
- EX[IT] Command
- F[ILES] Command
- FC Command
- FN Command
- FNL Command
- FREEZE Command
- HALT Command
- H[ELP] Command
- I Command
- IH Command
- INSPECT Command
- LMAP Command
- M Command
- MH Command
- Output-Device Syntax
- P[AUSE] Command
- PMAP Command
- PRV Command
- R Command
- S[TOP] Command
- T Command
- V Command
- VQ Command
- VQA Command
- = Command
- ? Command
- D Session Boundaries
- E Correspondence Between Debug and Inspect Commands
- F Sample Debug Sessions
- Glossary
- Index
Introduction
Debug Manual—421921-003
1-9
How to Determine Process State on a Trap or Signal
Debug Header Message on page 1-10. For more information about space identifiers,
see the appropriate server description manual for the processor that you are using.
Note. You cannot resume a process that entered Debug either because it received a
nondeferrable signal or because a synchronous trap occurred. A signal is nondeferrable if it
was generated by the system because the process cannot continue executing the instruction
stream. The only traps from which you can resume are the looptimer trap and the arithmetic
overflow trap, provided that the T and V bits are not both set in the ENV register.
Resuming from any of these nonresumable situations causes the process to be terminated
with the same Guardian Stop message or OSS wait status as would have been generated had
the signal or trap terminated the process without entering Debug. For additional information
about signals and traps, refer to Guardian Programmer’s Guide.
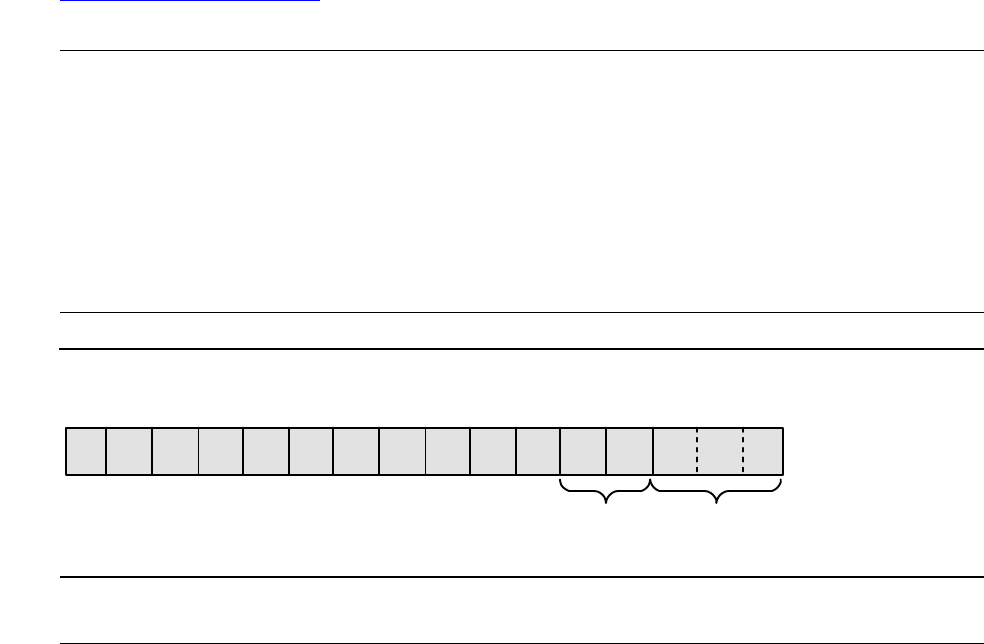
Figure 1-1. Environment Register (TNS Environment)
Field Description Bits Values
LS Library space ENV.<4> 0 = Code space
1 = Library space
PRIV Privileged ENV.<5> 0 = Nonprivileged
1 = Privileged
DS Data space ENV.<6> 0 = User
1 = System
CS Code space ENV.<7> 0 = User
1 = System
T Trap enable ENV.<8> 0 = Disable
1 = Enable
K Carry bit ENV.<9> 1 = Carry
V Overflow ENV.<10> 0 = No overflow
1 = Overflow
N Negative or numeric condition ENV.<11> See CC
Z Zero or alphabetic ENV.<12> See CC
CC Condition code ENV.<11:12> 10 < CCL (numeric)
01 = CCE (alpha)
00 > CCG (special)
RP Register stack pointer ENV.<13:15>
1514135
PRIV
4
LS
6
DS
7
CS
8
T
9
K
10
V
12
Z
11
N
RP
CC
VST0101.vsd










