Debug Manual
Table Of Contents
- What’s New in This Manual
- About This Manual
- 1 Introduction
- Execution Modes on TNS/R Systems
- What User Access Is Required for Debugging
- How to Make a Process Enter Debug
- How to Select Debug as the Debugger
- Why a Process Enters Debug
- How to Determine Process State on a Trap or Signal
- Ending a Debug Session
- What Appears in the Debug Header Message
- How to Use Debug
- How Debug Breakpoints Work
- 2 Using Debug on TNS/R Processors
- 3 Debug Command Overview
- 4 Debug Commands
- Command Summary
- A Command
- AMAP Command
- B Command
- BASE Command
- BM Command
- C Command
- CM Command
- D Command
- DJ Command
- DN Command
- EX[IT] Command
- F[ILES] Command
- FC Command
- FN Command
- FNL Command
- FREEZE Command
- HALT Command
- H[ELP] Command
- I Command
- IH Command (TNS/R Native and OSS Processes)
- INSPECT Command
- LMAP Command
- M Command
- MH Command (TNS/R Native and OSS Processes)
- P[AUSE] Command
- PMAP Command (Accelerated Programs)
- PRV Command
- R Command
- S[TOP] Command
- T Command
- V Command
- VQ Command
- VQA Command
- = Command
- ? Command
- A Error Messages
- B ASCII Character Set
- C Command Syntax Summary
- Register Syntax
- Expression Syntax
- Address Syntax
- A Command
- AMAP Command
- B Command
- BASE Command
- BM Command
- C Command
- CM Command
- D Command
- DJ Command
- DN Command
- EX[IT] Command
- F[ILES] Command
- FC Command
- FN Command
- FNL Command
- FREEZE Command
- HALT Command
- H[ELP] Command
- I Command
- IH Command
- INSPECT Command
- LMAP Command
- M Command
- MH Command
- Output-Device Syntax
- P[AUSE] Command
- PMAP Command
- PRV Command
- R Command
- S[TOP] Command
- T Command
- V Command
- VQ Command
- VQA Command
- = Command
- ? Command
- D Session Boundaries
- E Correspondence Between Debug and Inspect Commands
- F Sample Debug Sessions
- Glossary
- Index
Using Debug on TNS/R Processors
Debug Manual—421921-003
2-7
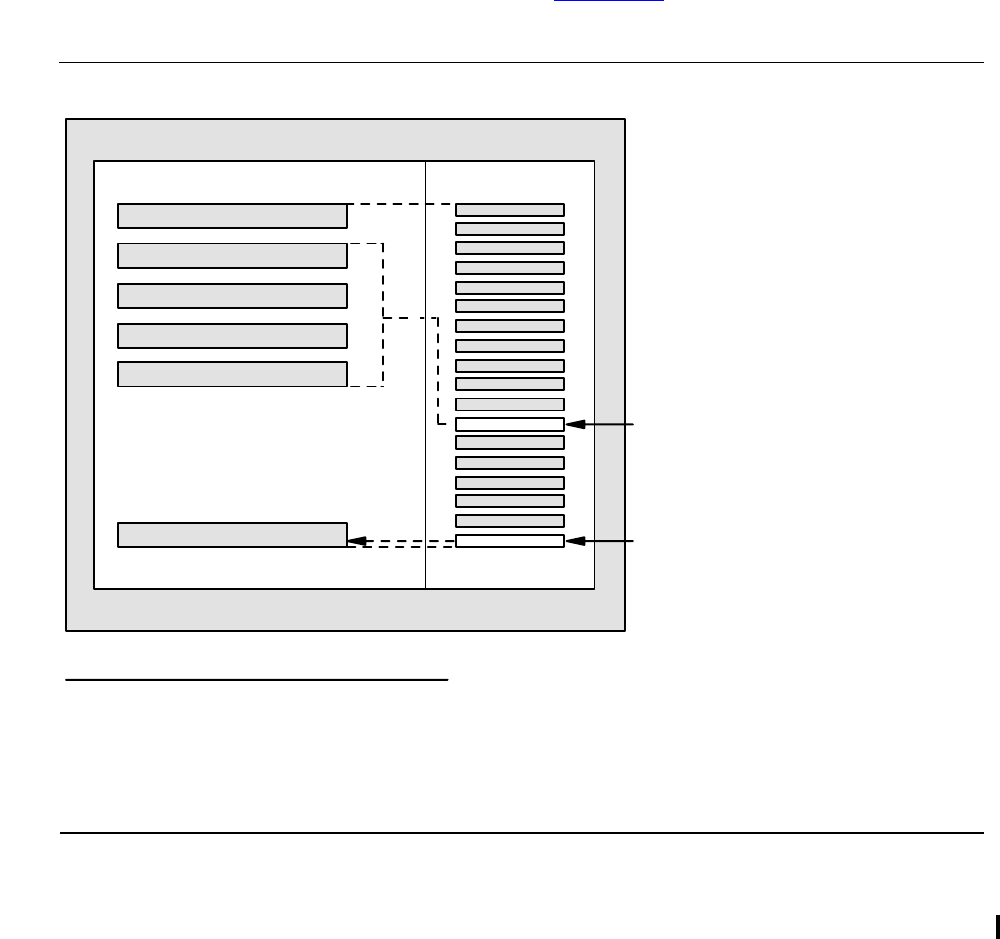
Setting RISC Breakpoints
Setting RISC Breakpoints
A RISC breakpoint is allowed on any valid RISC address. A RISC breakpoint in
accelerated code does not cause a corresponding TNS breakpoint to be set even
though a corresponding TNS instruction might exist. You set a RISC breakpoint by
using a B command that includes the 32-bit address mode. How RISC breakpoints
correspond to TNS instructions is illustrated in Figure 2-3, which shows setting
breakpoints in the accelerated user code area.
Rules About RISC Breakpoints
These rules about breakpoints apply to accelerated programs:
•
A breakpoint set on a TNS instruction also sets a breakpoint in the generated RISC
instruction.
•
Whether a TNS or RISC breakpoint is actually accessed depends on whether a
process is executing in TNS or accelerated execution mode. A TNS breakpoint
occurs in TNS execution mode; a RISC breakpoint occurs in accelerated execution
mode.
Figure 2-3. How RISC Breakpoints Correspond to TNS Instructions
BN 0x70 nnnnnn
BN 0x70 nnnnnn
User Code Area for ProcA
BN 0x70 nnnnnn specifies a RISC breakpoint
Register-Exact Point
TNS Instructions
RISC Instructions
//
Register-Exact Point
Legend
VST0203.vsd










