Expand Configuration and Management Manual (G06.24+)
Planning for ServerNet Clusters
Expand Configuration and Management Manual—523347-008
4-5
Examples of ServerNet Clusters Coexisting With
FOX Rings
Expand sees the NonStop K-series as only one hop away even when it is several hops
away. In addition, if a message has to travel between a NonStop S-series server and a
NonStop K-series server, and both FOX and ServerNet clusters are available, Expand
always chooses FOX because, based on time factors, Expand sees ServerNet cluster-
to-FOX transmissions as having a time factor of 1 plus 2 (3) but sees FOX-to-FOX
transmissions as having a time factor of just 2.
Grouping NonStop K-series servers together also speeds transactions.
ServerNet Cluster and FOX Ring Connected By One
NonStop S-Series System (Not Recommended)
The topology shown in Figure 4-2 is not recommended for connecting a ServerNet
cluster to an existing FOX ring. Processor use is higher whenever traffic flows between
\BBB, \CCC, or \EEE and \AAA, \DDD, or \FFF. For example, when \DDD requests
information from \CCC, four Expand line handlers are invoked: one in \DDD, two in
\HHH, and one in \CCC.
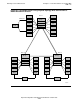
Figure 4-1. ServerNet Cluster Inside a FOX Ring
Note. You can extend the example shown in Figure 4-1 to multiple cluster switches and
servers.
\BBB #2
NonStop
S-series
\CCC #3
NonStop
S-series
\AAA #1
NonStop
S-series
\DDD #4
NonStop
K-series
\EEE #5
NonStop
K-series
\FFF #6
NonStop
S-series
\GGG #7
NonStop
S-series
\HHH #8
NonStop
S-series
Cluster
switch
VST068