Expand Configuration and Management Manual (G06.24+)
Subsystem Description
Expand Configuration and Management Manual—523347-008
18-34
Multi-CPU Routing Examples
•
When a new path comes up. (This is similar to what happens in normal paths when
a new path that has a lower TF is discovered.)
•
At configurable times during the day. You can use the SCF ALTER PROCESS,
AUTOREBALANCE command to specify when rebalancing should occur. Both the
time of day and the interval between rebalance attempts can be specified, allowing
you to schedule a rebalance when traffic is minimal.
•
Immediately. You can use the SCF RESET PROCESS command to cause an
immediate rebalance.
•
When a path goes down. (In this case, the rebalancing algorithm is not actually
used; instead, new connections are set up according to the current load.)
Multi-CPU Routing Examples
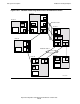
The routing decisions made for multi-CPU paths depend on each possible combination
of source and destination node; Figure 18-11 shows multi-CPU routing for these
combinations.
In Figure 18-11, the network includes four normal paths and two multi-CPU paths. A
multi-CPU path that consists of three paths is configured between node \B and node
\C, and a multi-CPU path that consists of two paths is configured between node \C and
node \E.