Expand Configuration and Management Manual (G06.24+)
Subsystem Description
Expand Configuration and Management Manual—523347-008
18-41
Outgoing Traffic Flow
$NCP and Passthrough Traffic Flow
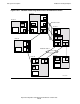
Figure 18-13 illustrates the path of outgoing $NCP and passthrough traffic.
The message system uses the NRT to route passthrough packets from the incoming
Expand line-handler process (the one that received the packets) to the Expand line-
handler process that can most efficiently transmit the packets to the destination
system.
Similarly, the message system uses the NRT to route locally generated $NCP packets
to the Expand line-handler process that can most efficiently transmit the message to
the $NCP at a neighboring node.
When the Expand line-handler process acquires a passthrough or $NCP packet from
the message system, it queues the packet to its list of pending $NCP/passthrough
traffic for the appropriate destination node. The Expand line-handler process maintains
a different pending $NCP/passthrough traffic list for each path.
The Expand line-handler process moves passthrough and $NCP packets from its list of
pending $NCP/passthrough traffic to its list of outgoing $NCP/passthrough traffic.
Note. Requests are formatted into request data packets, or LRQs. Replies are formatted into
reply data packets, or LCMPs. LRQs and LCMPs are explained in Protocol Packet Types on
page 18-13.
Figure 18-13. Flow of Outgoing $NCP and Passthrough Traffic
021CDT .CDD
Queue packets to
$NCP/pass-through pending
list for destination node
Use memory from buffer
pool and queue packets to
outgoing $NCP/pass-
through packets list
Send packets
Release buffer
pool