FORTRAN Reference Manual
Memory Organization
FORTRAN Reference Manual—528615-001
12-5
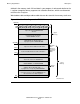
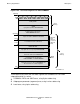
Upper Memory
Upper Memory
The upper memory area (the “upper” 32K words of the user data segment) is optionally
available for
•
Common data specified by the HIGHCOMMON directive
•
Control information specified by the HIGHCONTROL and HIGHBUFFER directives
Access to upper memory is by indirect addressing only. FORTRAN stores only word-
addressable data in upper memory.
Storage Areas
The Binder load map in your program listing includes a list of the data blocks that
FORTRAN allocates to hold program data as well as data blocks that hold internal data
used by the FORTRAN run-time environment. The names and contents of these data
blocks depend on whether you compile your program with ENV COMMON or ENV
OLD in effect. Table 12-1 lists the data blocks allocated by FORTRAN. Table 12-2 on
page 12-6 lists the compiler directives that affect how FORTRAN allocates data.
Table 12-1. Data Blocks
Block OLD COMMON
Directives That Affect Block’s
Location and Size
#FLUT X – HIGHCONTROL
#PUCB X – HIGHCONTROL
#RUCB X – HIGHCONTROL
FCBs – X HIGHCONTROL
#HIGHBUF X – HIGHBUFFER
#LOWBUF X – LOWBUFFER
#G0 X – none
#MCB – X HIGHCONTROL, HIGHBUFFER
#CRE_HEAP – X HIGHBUFFER
#CRE_GLOBALS – X none
Common blocks X X HIGHCOMMON, LARGECOMMON
COMMON#POINTERS X X LARGECOMMON
#RECEIVE – X RECEIVE
X The data block is used in the specified environment
– The data block is not used in the specified environment