GDSX (Extended General Device Support) Manual
Overview of GDSX
Extended General Device Support (GDSX) Manual—529931-001
1-13
Indirect Terminal Access
individual devices on the line do not. Some data communication products that do not
allow direct addressing of terminals on line are:
•
CP6100 ADCCP/NRM
•
CP6100 Bisync Multipoint
•
Envoy
•
EnvoyACP/XF
GDSX applications using these products cannot use a direct interface of
DEVICE^HANDLER tasks with I/O processes—LINE^HANDLER tasks must also be
used to implement communication protocols and to manage the line so that different
threads accessing the line do not interfere with each other.
When an application using Pathway/iTS and GDSX is started, the GDSX process is
run first. For example, the following commands can be issued to run a GDSX object
named $GDS:
> PARAM MAXLINES 1
> RUN GDSE /NAME $GDS, NOWAIT/
The MAXLINES configuration parameter there is to be a maximum of one line in the
configuration.
Then SCF is used to configure the LINE and devices under the line, and to START the
LINE. Here is an example of a configuration having one LINE and three SUs under the
LINE:
-> SCF
-> ADD LINE $GDS.#LINE1, ACCESSNAME $IOP1
-> ADD SU $GDS.#LINE1.DEV1
-> ADD SU $GDS.#LINE1.DEV2
-> ADD SU $GDS.#LINE1.DEV3
-> START LINE $GDS.#LINE1
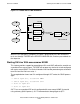
When the LINE is started in SCF, GDSX refers to the line’s access name (the file
associated with the LINE object), opens the file ($IOP1 in this case), and creates a
LINE^HANDLER task to manage communication with the devices on the line, as
shown in Figure 1-7. All devices on the LINE are then available for access.
Figure 1-7. Indirect Terminal Access Transaction Flow
SCF
START LINE
$GDS.#LINE1
Open
$IOP1
VST007.VSD
$GDS IOP