Introduction to ENFORM
Compiling the Query
How ENFORM Works
058051 Tandem Computers Incorporated 3–3
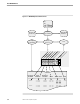
Figure 3-1 illustrates that the following sequence of steps is involved in processing an
ENFORM LIST query:
1. Query compilation by the compiler/report writer process.
2. Transfer of control and dictionary-derived file information to the query processor:
a server process that accesses the database files specified in the query.
3. The production of a target (work) file by the query processor. The target file is the
result of the query; it contains items of information (both from the database and
derived) that will appear on the report.
4. Transfer of control and the target file back to the compiler/report writer process to
format and produce the report.
Basically, these steps illustrate that you should think of ENFORM as providing two
logical functions: (1) report formatting and writing, and (2) query processing where
the result of the query is a target file that will be processed by the compiler/report
writer in step 4.
Compiling the Query The compiler/report writer process has two logical functions or phases: (1) compiling
the query and (2) formatting and writing the report. The purpose of the first phase is to
ensure that the query processor receives the information that it needs to process the
query.
In the compilation phase, your query specifications are first checked for syntactical
correctness: do they obey the rules of the language? Any errors detected at this point
will stop query processing and result in a syntax error for the query.
If the source specifications are correct, they are transformed into an intermediate form
that can be interpreted by the query processor. The intermediate form is a compiled
representation of the query. It contains information:
From the dictionary about the files and fields needed to build the target file.
That will be used to construct target records by the query processor; every target
record looks like a template of the specifications in the query.
About related files.
About qualifications in the query specification that will limit the number of
records read from the database and written to the target file.
The compiled query is then sent to the query processor (as a message) using standard
interprocess I/O.
The compiler/report writer also builds a table containing information that will allow it
to format and produce the report during its report writing phase—when it receives
control back from the query processor.