Introduction to Networking for NonStop S-Series Servers
HP NonStop S-Series Systems Network Architecture
(SNA) Network Connections
Introduction to Networking for HP NonStop S-Series Servers—520670-005
7-3
Subarea Networking
portions of a transaction among multiple programs within a network. The programs
coordinate the distributed processing by exchanging control information or data.
Subarea Networking
An SNA network can have multiple subareas; each subarea has an address, and all
addresses within a subarea are unique. A subarea can consist of either a host (node
type 5) and its resources or a communications controller (node type 4) and its
resources. Thus, a domain that includes a communications controller can include
multiple subareas: the host is defined as one subarea, and the controller and its
resources are defined as another subarea.
Peer-to-Peer Networking
Advanced peer-to-peer networking (APPN) is an extension of SNA that enables a
variety of SNA systems (such as PS/2, AS/400, System/38, System/370, and
System/390) to communicate as peers, without the control of a host. The peer systems
must all have the requisite software to function as type 2.1 nodes.
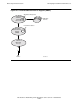
Figure 7-1. SNA Terminology Illustrated
Communication
s
Controller
SNA Host
Node Type
4
Node Type
5
Cluster
Controller
Node Type
2
3270 Devices
Subarea Networking Peer-to-Peer Networking
LEN Node
End Node
Network
Node
Network
Node
Network
Node
VST905.vsd