Introduction to Networking for NonStop S-Series Servers
HP NonStop S-Series Systems Network Architecture
(SNA) Network Connections
Introduction to Networking for HP NonStop S-Series Servers—520670-005
7-12
SNAX/APN
IBM to HP
To send data to BCOM on the NonStop S-Series server, BCOM on the IBM system
passes the data to VTAM. VTAM places the data on the ESCON channel.
The PCI/ESCON interface card on the NT platform takes the data off the ESCON
channel and gives the data to ES Connect. ES Connect saves the data until SNAX
makes a request for it.
When Titanium gives the data to SNAX, SNAX forwards it to the application.
SNAX/APN
SNAX/APN enables a NonStop S-series server to act as an SNA type 2.1 node. The
base product acts as an LEN node; the extended version, SNAX/APN-EN, can act as
an end node. Using SNAX/APN, a NonStop S-series server can
•
Communicate with SNA type 2.1 nodes using advanced program-to-program
communication (APPC). The type 2.1 nodes can be attached directly or can be
accessible through an attached APPN network node server. HP applications can
use logical units (LU) sessions, typically through SNAX/APC.
•
Attach to either a subarea or APN network. (Note that SNAX/APN End Node can
only attach to an APPN network.)
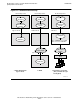
Figure 7-5 on page 7-13 shows SNAX/APN connectivity.
For simplicity, the SNAX service manager processes, ServerNet wide area network
(SWAN) concentrator, and SNA communications controllers are omitted. Also, the
process shown in a single NonStop S-series server can be distributed across an
Expand network.
If a NonStop application sends a LOGON request to another application, XLF is
required, and if the NonStop applications wants to receive LOGON requests then XLF
or ELF is required.