Introduction to Networking for NonStop S-Series Servers
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Network
Connections
Introduction to Networking for HP NonStop S-Series Servers—520670-005
8-3
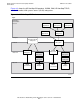
A Brief Look at OSI
Each of the seven layers performs a distinct function, described briefly below:
Application Layer Gives an application program access to the OSI network. This
layer consists of two kinds of service elements: Those
common to many applications constitute the Association
Control Service Element (ACSE); those used for specific
applications are called Application Service Elements (ASEs),
of which FTAM and X.400 are examples. The term
association refers to an Application-Layer connection.
Presentation Layer Defines the format and encoding of information sent over the
communications medium. Compensates for differences in
data representation among communicating systems and
devices.
Session Layer Enables an application program to organize and synchronize
the exchange of information with other application programs.
Transport Layer Provides reliable transfer of data between systems. Selects
among available Network Layer services and defines
transport classes, which tailor the responsibilities of the layer
to different network environments.
Network Layer Accomplishes the routing of information through the network,
including functions to support transfer of data across different
subnetworks. In connection-oriented service, the Network
Layer establishes a long-term connection between
communicating entities and maintains information to relate the
messages, ensuring that pieces of the same message arrive
at their destination in sequence and without error. In
connectionless service, the Network Layer transfers data
without retaining context information.
Data-Link Layer Manages the flow of data over physical links and performs
link-level error-recovery and synchronization. Includes media
access control (MAC) procedures, which coordinate the
sharing of a communications medium by stations on a local
area network (LAN).
Physical Layer Specifies connections between physical entities, such as type
of cabling or electrical interface.