Introduction to Networking for NonStop S-Series Servers
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Network
Connections
Introduction to Networking for HP NonStop S-Series Servers—520670-005
8-9
Message Handling System (OSI/MHS)
following service classes: file transfer, file management, file transfer and management
(which includes subsets of file transfer and file management), and file access.
Additionally, FTAM defines two groups of attributes: file attributes, which are
characteristics of the file itself (such as who created it and when it was last modified),
and activity attributes, which apply only during an association (for instance, the
identity of the current requester of FTAM services). HP FTAM supports a range of
attributes in both these groups.
The manuals describing HP FTAM provide much more detailed specifications of the
implementation.
Unlike most HP subsystems, HP FTAM is managed through two Subsystem Control
Facility (SCF) interfaces: the HP NonStop OSI/Application Manager (APLMGR)
subsystem and the FTAM subsystem itself. The APLMGR subsystem allows you to
configure and manage HP FTAM processes, and the FTAM subsystem allows you to
monitor initiator and responder processes and manage the subdevices of those
processes.
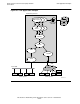
Message Handling System (OSI/MHS)
HP NonStop OSI/MHS is an implementation of the ITU–T X.400 (formerly CCITT)
Recommendation and the ISO standard for Message Handling Systems (MHSs). It
complies with the 1988 versions of the CCITT standards and can interoperate with
systems that follow the 1984 standards. It also complies with GOSIP and the
equivalent European standards for MHSs.
The protocols for communication among OSI/MHS components are listed and
described below:
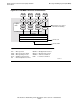
Note. Figure 8-3 on page 8-10 shows HP NonStop S-series servers connected by OSI rather
than by the Expand subsystem. You can also run the Expand subsystem between the
systems—even on the same physical circuits—for use by management applications and others
that require continuous availability.
Protocol As Used by OSI/MHS
P1 The protocol between two Message Transfer Agents (MTAs)
P2 The protocol between two User Agents (UAs) for the exchange of
interpersonal messages and notifications across the network (1984 or 1988)
P3 The protocol between a UA and an MTA when the UA directly requests MTA
services
P7 The protocol between a UA and a Message Store (MS)
P22 The protocol between two UAs (1988)
Pedi The protocol between two UAs when objects are used for electronic data
interchange (EDI)