Introduction to Networking for NonStop S-Series Servers
Communications Product Concepts and
Components
Introduction to Networking for HP NonStop S-Series Servers—520670-005
2-12
Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area
Networks (WANs)
Processes that use the SLSA subsystem to send and receive data on a LAN attached
to a NonStop S-series server are called LAN service providers. Three directly
attached LAN service providers—the NonStop TCP/IP subsystem, the Port Access
Method (PAM) subsystem, and NonStop IPX/SPX—are currently supported. They
provide access for the following:
LAN clients are processes, user applications, and subsystems that use the SLSA
subsystem and related LAN providers to connect to an Ethernet, a Fast Ethernet,
Gigabit Ethernet, or a token-ring LAN attached to a NonStop S-series server. For
example, the WAN subsystem is a client of the SLSA subsystem because the SLSA
subsystem provides the WAN subsystem access to the SWAN concentrator through
the LAN. The WAN subsystem is described in Wide Area Network (WAN) Subsystem
on page 2-14.
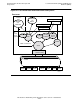
Figure 2-4 shows how the SLSA subsystem relates to several other communications
subsystems
QIO application
program interface
(API) clients
These are protocol subsystems that communicate with a LAN
transport service provider directly through QIO. Currently, these
are:
•
The Expand subsystem, which connects through the QIO
API to NonStop TCP/IP in order to provide Expand-over-IP
connections. The Expand subsystem is described in
Section 5, Expand Network. NonStop TCP/IP is described in
Section 10, TCP/IP Network Connections.
•
WAN IOP drivers, which connect through the QIO API to
NonStop TCP/IP to provide access to remote ServerNet
wide area network (SWAN) concentrators.
•
NonStop IPX/SPX, which provides connectivity to a Novell
NetWare LAN. IPX/SPX is described in Section 9, Local
Area Network (LAN) Connections.
•
The PAM subsystem, which provides programmatic access
to Ethernet and token-ring LANs. The OSI/AS, OSI/TS,
SNAX/XF, and SNAX/APN subsystems interface to SLSA
through the PAM subsystem. PAM is described in Port
Access Method (PAM) Programmatic Interfaces on
page 9-3.
•
SNAX over Ethernet uses QIO to communicate directly with
SLSA and eliminate the need for the PAM subsystem.
Sockets Library
applications
These are user applications and HP utilities (such as TELSERV
and FTP) that use the sockets library to establish remote
connections and communicate through NonStop TCP/IP and
IPX/SPX.