Introduction to Networking for NonStop S-Series Servers
Application Programming With Communications
Products
Introduction to Networking for HP NonStop S-Series Servers—520670-005
3-4
Application Architecture Examples
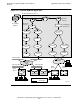
Figure 3-2 on page 3-5 illustrates a railway reservation system. Transactions are
initiated at terminals connected to UNIX workstations over either an Ethernet LAN or
an X.25 packet-switched data network (PSDN). Depending on the nature of a
transaction, the UNIX workstation routes it to either the NonStop S-series server (in the
case of a seat-reservation transaction) or another system on the LAN or PSDN (in the
case of a railway timetable query).
The railway reservation application is a Pathway application operating on an SQL
database. The application uses HP Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) products for
connection to LANs and wide area networks (WANs). For the LAN, the OSI products
are client applications of the Port Access Method (PAM) subsystem. The PAM
subsystem uses the ServerNet LAN systems access (SLSA) subsystem to send and
receive data on a LAN. For the WAN, the OSI products use the HP X.25 Access
Method (X25AM).
There is one communications programming task on the NonStop S-series server: A
front-end process using OSI/TS supports cooperative processing between requesters
on the UNIX workstations and database servers on the NonStop S-series server. The
same application code can run over either network.
The fact that each OSI/TS process uses a different instance of the PAM subsystem or
X25AM represents an application designer’s choice, not a configuration restriction.
Multiple instances of OSI/TS can use the same input/output process (IOP), and one
instance of OSI/TS can use both X25AM and the PAM subsystem.