Introduction to TRANSFER Delivery System
Summary of the TRANSFER Delivery System The TRANSFER Delivery System
1-20 109426—Introduction to TRANSFER Delivery System
Summary of the TRANSFER Delivery System
In summary, with the Tandem TRANSFER delivery system, you are ensured of:
■ Geographic independence
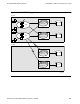
TRANSFER lets you define a group of correspondents who can be on a single
system or on any network node where TRANSFER is installed. With one request to
TRANSFER, a process can send a package to multiple destinations anywhere in an
EXPAND network.
■ Flexible transfer of data
TRANSFER disregards the content of packages, as well as the software used to
develop and run the communicating processes. For example, an inventory control
application written in COBOL can communicate with a financial application written
in FORTRAN.
■ Reliable package delivery
With TRANSFER, you know that any package sent is delivered exactly once to each
recipient.
■ A package is time-stamped to indicate the earliest and latest times at which it
can be delivered. If a package cannot be delivered within the timeframe,
TRANSFER notifies the sender and returns the package.
■ Even in the case of a hardware failure, a package is never lost or delivered twice
to the same recipient.
■ A recipient of a package need not be present to receive it. Recipients pick up
packages at their own convenience.
■ If a recipient’s node is unavailable when TRANSFER tries to deliver a package,
the package is stored on the sending node and queued for delivery until the
recipient’s node becomes available.
■ TRANSFER can certify the delivery of a package so that the sender receives a
certification on behalf of each recipient.
■ A package can be assigned a priority so that if many packages are sent within a
short time, higher priority packages are delivered first.
■ Database integrity
TRANSFER uses TMF to ensure the consistency of database files.
■ If a failure occurs while a package is being delivered, the transaction is backed
out and put on the HELD queue for later retry of delivery.
■ Requesters to TRANSFER also use TMF to ensure the consistency of the files
that contain stored packages, distribution lists, and configuration data.
■ Files can be reconstructed in the event of a system crash.