iTP Secure WebServer System Administrator's Guide (Version 7.0)
iTP Secure WebServer System Administrator’s Guide—523346-012
D-1
D Security Concepts
This appendix describes basic concepts relevant to setting up and administering the
iTP Secure WebServer:
•
Open Network Security on page D-1
•
Cryptographic Techniques on page D-3
•
Managing Key Certificates on page D-5
•
Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) on page D-7
•
Private Communications Technology (PCT) on page D-9
•
Comparing SSL and PCT on page D-9
Open Network Security
This section discusses these security topics as they relate to security systems on open
networks:
•
Encryption on page D-1
•
Authentication on page D-2
Encryption
Encryption is the transformation of data into a form that only persons who have access
to the proper decryption key can read. Encryption ensures privacy by keeping
information hidden from anyone for whom it is not intended. For example, to keep
competitive bidding data from falling into the hands of your rivals, you might want to
encrypt your data before transmitting it to a prospective client across a public
communications link. Or to keep your department’s personnel records secure, you
might want to encrypt these records before storing them on hard disk.
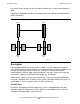
In general, encryption works as described and as shown in Figure D-1 on page D-2:
Romeo wants to send a private message to Juliet over a public communications link.
Romeo encrypts his message (called the plaintext) with an encryption key, and then
sends the encrypted message (called the ciphertext) to Juliet. Using a decryption key
associated with the encryption key used by Romeo, Juliet decrypts Romeo’s ciphertext
back into human-readable form.