Jolt 1.2 Developer's Guide
Table Of Contents
- Jolt for NonStop(TM) TUXEDO Developer's Guide
- Jolt for NonStop(TM) TUXEDO Developer's Guide
- About This Guide
- 1. Introducing Jolt
- 2. Installing Jolt
- 3. Configuring the Jolt System
- 4. Bulk Loading NonStopTM TUXEDO Services
- 5. Using the Jolt Repository Editor
- 6. Using the Jolt Class Library
- 7. Using JoltBeans
- 8. Using Servlet Connectivity for NonStopTM TUXEDO
- 9. Using Jolt 1.2 ASP Connectivity for NonStopTM TUXEDO
- A. NonStopTM TUXEDO Errors
- B. System Messages
- Index
Security and Encryption
Authentication and key exchange data are transmitted between Jolt clients and the JSL/JSH using the Diffie-Hellman key
exchange. All subsequent exchanges are encrypted using RC4 encryption. International packages use a DES key exchange and a
128-bit key, with 40 bits encrypted and 88 bits exposed.
Programs using 128-bit encryption cannot be exported outside the United States without proper approval from the United States
government. Customers with intranets extending beyond the United States cannot use this mode of encryption if any internal
clients are outside the United States.
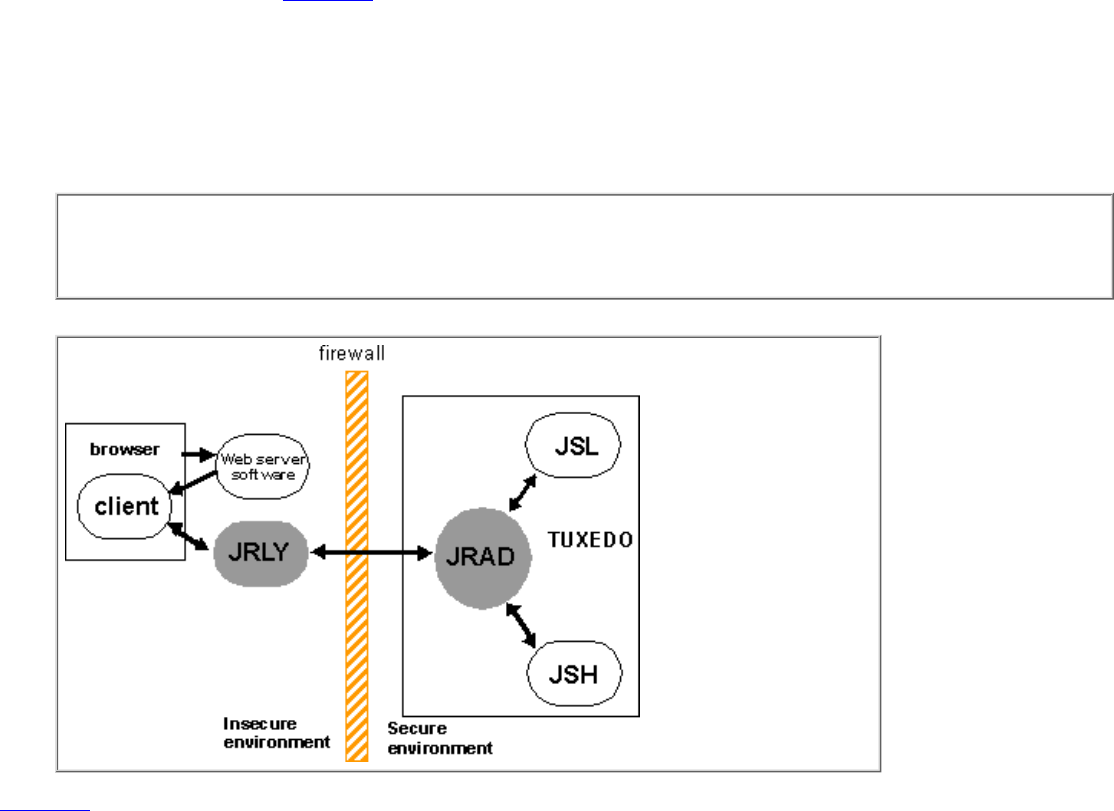
Jolt Relay
The combination of the Jolt Relay (JRLY) and its associated Jolt Relay Adapter (JRAD) is referred to as the Internet Relay. Jolt
Relay is a component that routes messages from a Jolt client to a JSL or JSH. This eliminates the need for the JSH and
NonStop
TM
TUXEDO to run on the same machine as the Web server (generally considered as insecure). The Jolt Relay consists
of two components illustrated in Figure 3-2:
Jolt Relay (JRLY). The JRLY is the Jolt Relay front-end. It is not a NonStop
TM
TUXEDO client or server and is not
dependent on the NonStop
TM
TUXEDO version. It is a stand-alone software component. It requires only minimal
configuration to allow it to work with Jolt clients.
●
Jolt Relay Adapter (JRAD). The JRAD is the Jolt Relay back-end. It is a NonStop
TM
TUXEDO system server, but does not
include any NonStop
TM
TUXEDO services. It requires command line arguments to allow it to work with the JSL and the
NonStop
TM
TUXEDO system.
Note
The Jolt Relay is transparent to Jolt clients and Jolt servers. A Jolt server can simultaneously connect to intranet clients
directly, or via the Jolt Relay to Internet clients.
Figure 3-2. Jolt Internet Relay Path
●
Figure 3-2 shows how a browser connects to the Web server software and downloads the Jolt applets. The Jolt applet or client
connects to the JRLY on the Web server machine. The JRLY forwards Jolt messages across the firewall to the JRAD. The JRAD
selectively forwards messages to the JSL or appropriate JSH.
Jolt Relay Failover
These are the two points of failovers associated with JRLY:
Jolt Client to JRLY connection failover
If one server address does not result in a successful session, the failover function allows the Jolt Client API to connect to
the next free (unconnected) JRLY specified in the argument list of the API. To enable this failover, multiple JRLY
●










