Jolt 1.2 Developer's Guide
Table Of Contents
- Jolt for NonStop(TM) TUXEDO Developer's Guide
- Jolt for NonStop(TM) TUXEDO Developer's Guide
- About This Guide
- 1. Introducing Jolt
- 2. Installing Jolt
- 3. Configuring the Jolt System
- 4. Bulk Loading NonStopTM TUXEDO Services
- 5. Using the Jolt Repository Editor
- 6. Using the Jolt Class Library
- 7. Using JoltBeans
- 8. Using Servlet Connectivity for NonStopTM TUXEDO
- 9. Using Jolt 1.2 ASP Connectivity for NonStopTM TUXEDO
- A. NonStopTM TUXEDO Errors
- B. System Messages
- Index
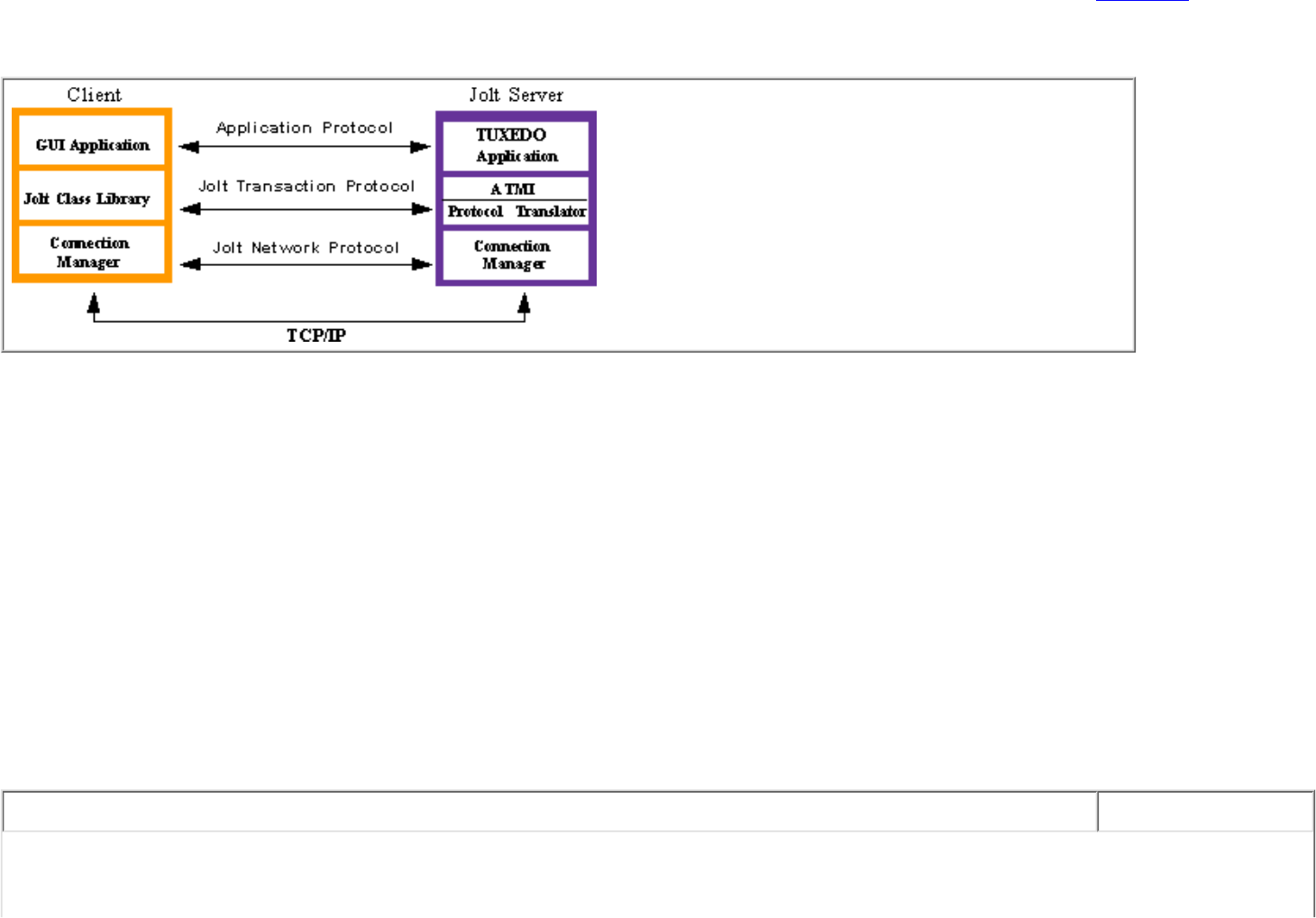
Jolt Client/Server Relationship
Jolt works in a distributed client/server environment and connects Java clients to NonStop
TM
TUXEDO-based applications. Figure 6-1 illustrates the
client/server relationship between a Jolt program and the Jolt Server.
Figure 6-1. Jolt Client/Server Relationship
The Jolt Server acts as a proxy for a native NonStop
TM
TUXEDO client, implementing functionality available through the native NonStop
TM
TUXEDO client. The Jolt Server accepts requests from Jolt clients and maps those requests into NonStop
TM
TUXEDO service requests through the
NonStop
TM
TUXEDO ATMI interface. Requests and associated parameters are packaged into a message buffer and delivered over the network to
the Jolt Server. The Jolt Connection Manager handles all communication between the Jolt Server and the Jolt applet using the Jolt Transaction
Protocol. The Jolt Server unpacks the data from the message, performs any necessary data conversions, such as numeric format conversions or
character set conversions, and makes the appropriate service request to NonStop
TM
TUXEDO as specified by the message.
Once a service request enters the NonStop
TM
TUXEDO system, it is executed in exactly the same manner as any other NonStop
TM
TUXEDO
request. The results are returned through the ATMI interface to the Jolt Server, which packages the results and any error information into a message
that is sent to the Jolt client applet. The Jolt client then maps the contents of the message into the various Jolt client interface objects, completing the
request.
On the client side, the user program contains the client application code. The Jolt Class Library packages a JoltSession and JoltTransaction, which in
turn handle service requests.
The following table describes the client-side requests and Jolt Server-side actions in a simple example program.
Table 6-1. Jolt Client/Server Interaction
Jolt Client Jolt Server










