NetBatch Manual
NetBatch Introduction
NetBatch Manual—522460-004
1-11
Job Tracking, Control, and Termination
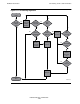
Table 1-1. Scheduling Algorithm Description
Item Description
1. Begin. These trigger events make the scheduler start the job selection and
startup procedure:
•
Submission of a job
•
Satisfaction of a job’s timing attributes (AFTER, AT, CALENDAR,
EVERY, and WAIT)
•
Alteration of a job’s HOLD attribute from ON to OFF
•
Completion of job startup or termination of a job
2. Any jobs ready to
run?
The scheduler maintains an internal, prioritized list of jobs that are
ready to run. It identifies the first (highest priority) job on the list and
goes to Item 3. If there are jobs on the list, the scheduler exits the
procedure.
Ready to run jobs are in the RUNNOW, RUNNEXT, or READY states.
Of these, RUNNOW jobs have the highest priority, followed by
RUNNEXT then READY. The scheduler determines the priority of
jobs with the same state from their SELPRI attributes. For jobs with
the same state and SELPRI attribute, the scheduler determines
priority by submission time on a first-in, first-out basis.
3. Select next
available executor.
4. Executor
selected?
The scheduler attempts selection from database file EXECUTOR of
the next executor. If executor selection is successful, the scheduler
goes to item 7. If unsuccessful (no more executors to select), the
scheduler goes to item 5.
5. Job from item 2
RUNNOW?
6. Create temporary
executor.
If the scheduler did not select an executor at item 3, it checks if the
job identified at item 2 has a state of RUNNOW. If so, the scheduler
creates a temporary executor for the job and goes to item 9.
Otherwise, the scheduler exits the procedure.
7. State ON? If the scheduler selects an executor at item 3, it checks if the
executor’s state is ON. If so, it goes to item 8. Otherwise, the
scheduler returns to item 3.
8. Class * attribute? The scheduler checks if the selected executor’s CLASS attribute
value is * (asterisk), meaning any class. If it is, the scheduler goes to
item 9. Otherwise, the scheduler goes to item 10.
9. Select job from
item 2.
The scheduler selects the job identified at item 2 and goes to item 15.
10. Select next
class.
11. Class selected?
The scheduler attempts selection from database file JOBCLASS of
the next class associated with the executor from item 3. If class
selection is successful, the scheduler goes to item 12. If unsuccessful
(no more classes to select), the scheduler returns to item 3.