NET/MASTER Management Services (MS) System Management Guide
INMC Conceptual Overview
Supporting Remote Operations
9–2 105744 Tandem Computers Incorporated
INMC Conceptual
Overview
Before learning how to configure an INMC link, you may find that a conceptual
overview of INMC helps you to understand the reasoning behind the configuration
procedures.
Functions and Features of
INMC
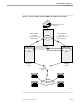
INMC provides a peer-level, logical connection to remote management applications,
irrespective of any underlying communications protocol(s) used to connect the
computers on which the management applications execute. A single link to a remote
Tandem computer can use SNA, X.25, and Expand lines simultaneously. The ability to
simultaneously use different protocols enables you to achieve the maximum level of
data transfer using the communications hardware and software that you already own;
it also minimizes restrictions on the communications software and hardware you
purchase in the future.
Remote Operator Control (ROC)
INMC links enable authorized users to send commands to a remote management
application by using the ROUTE command. Authorized users can also log on to a
remote NonStop NET/MASTER MS system by issuing the SIGNON link-name
command. (Refer to the NonStop NET/MASTER MS Operator’s Guide for a discussion
of use of the commands. Refer to the NonStop NET/MASTER MS Command Reference
Manual for a complete description of the commands.) The NonStop NET/MASTER
MS component that supports the ROUTE, SIGNON link-name, and SIGNOFF
commands is called the Remote Operator Control (ROC).
ROC is available by default. If you want to disable use of the ROC component, refer to
Section 3, “Configuring NonStop NET/MASTER MS,” for instructions. Refer to
Section 4, “Managing User Access and Privileges,” for an explanation of the procedure
for allowing user access to a remote management application.
Inter-System Routing (ISR)
An INMC link also supports exchange of solicited and unsolicited messages with
remote management applications. The NonStop NET/MASTER MS component that
processes the flow of these messages is called the Inter-System Routing (ISR). Like
ROC, ISR is available by default. If you want to disable use of ISR, refer to Section 3,
“Configuring NonStop NET/MASTER MS,” for instructions.
Overview of INMC Data
Transfer
ROC and ISR forward information destined for a remote management application to
INMC. When INMC receives the information, it divides the data into internally
formatted blocks of 1024 bytes. INMC sends a block to each available data transfer
unit in a circular fashion until INMC has sent all of the information destined for the
remote management application. Transfer units can include the following:
SNA logical units (LUs), if the data transfer occurs over an SNA line
X.25 virtual circuit units, if the data transfers occurs over an X.25 line
The remote process responsible for INMC processing, if the data transfer occurs
over an Expand line (or among NonStop NET/MASTER MS systems on the same
computer)