NonStop S-Series Operations Guide (G06.27+)
Determining Your System Configuration
HP NonStop S-Series Operations Guide—522459-008
2-26
Using SCF to Determine Your System Configuration
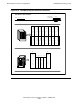
<portid>
is the slot number and port number mapped as:
<adapter>
is a 2-digit number in the range 00 through 99.
System planning and configuration staff at your site likely will change or expand on the
preconfigured file-naming conventions that HP provides, typically by establishing
naming conventions for configuring such objects as storage devices, communication
processes, and adapters. These conventions should simplify your monitoring tasks by
making process or object functions intuitively obvious to someone looking at the object
name. For example, in your environment, tape drives might be named $TAPEn, where
n is a sequential number. The SCF Reference Manual for G-Series RVUs lists HP
reserved names that cannot be changed or used for other objects or processes in your
environment.
Using SCF to Determine Your System Configuration
SCF is one of the most important tools available to you as a system operator. SCF
commands configure and control the objects (lines, controllers, processes, and so on)
belonging to each subsystem running on the NonStop S-series server. You also use
SCF to display information about subsystems and their objects.
SCF accepts commands from a workstation, a disk file, or an application process. It
sends display output to a workstation, a file, a process, or a printer. Some SCF
commands are available only to some subsystems. An overall SCF reference is the
SCF Reference Manual for G-Series RVUs. Subsystem-specific information appears in
a separate for each subsystem. For a partial list of these manuals, refer to Appendix C,
Related Reading.
More details about the functions of SCF appear in Subsystem Control Facility (SCF) on
page B-5.
Slot
Number
Port
Number <portid>
Slot
Number
Port
Number <portid>
51 0 0 53 0 8
51 1 1 53 1 9
51 2 2 53 2 A
51 3 3 53 3 B
52 0 4 54 0 C
52 1 5 54 1 D
52 2 6 54 2 E
52 3 7 54 3 F