NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual (G06.24+)
Memory Addressing and Access
HP NonStop S-Series Server Description Manual—520331-003
4-2
The Process Address Space
The Process Address Space
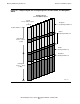
The virtual memory system of each processor in the NonStop S-series servers
provides a 4-GB virtual address space, as illustrated in Figure 4-1. Virtual memory is
arranged as multiple process address spaces. These address spaces are primarily
assigned to the various processes executing in the processor. However, only one such
space can be the current one.
These spaces are not exclusively for “processes”—the operating system claims one
process address space for use by interrupt handlers (which are not processes).
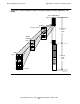
The 256 most recently active process address spaces (including the current one) have
special identifiers that make them eligible to have their relative virtual addresses
translated to physical addresses.
Each process address space is divided into a nonprivileged space (the lower 2 GB of
virtual addresses) and a privileged space (the higher 2 GB of virtual addresses). Each
of these spaces can have areas that are either global or nonglobal. Global addresses
have the same data in all process address spaces.
Privileged addresses can be accessed only by processes that are executing in
privileged mode. The privileged space, being mostly a global space, is used to address
system elements. Such elements include physical memory, resident privileged
procedures, and system data. Much of the privileged address space is devoted to
providing “absolute” addresses for segments that also have addresses in nonprivileged
space.
The nonprivileged space is used primarily to address the code and data for a given
process. Such code and data might or might not be shared among processes,
depending on specific applications. However, those elements that are designated as
global are always shared. These would include all nonprivileged or nonresident
system library procedures
Note. In publications describing RVUs prior to G05.00, the process address space was
referred to as the process data space, and nonprivileged space and privileged space were
referred to as user space and kernel space, respectively. These terminology changes reflect
current industry standard usage.